Technology
Key Challenges for Safaricom’s M-PESA Global Expansion in Ethiopia
Safaricom must overcome these significant challenges, including regulatory barriers, local competition, infrastructure limitations, and cultural hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges will determine the long-term success of the service in Ethiopia, while opening the door to broader regional growth.

: Safaricom’s M-PESA Global expansion into Ethiopia brings promising opportunities but faces key challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition from Telebirr, low mobile money penetration, and infrastructure limitations. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for driving financial inclusion and cross-border trade
By Charles Wachira
Safaricom’s expansion of M-PESA Global into Ethiopia presents numerous opportunities, there are several challenges that both Safaricom and Ethiopia could face in this process:
1. Regulatory Environment Government Regulations: Ethiopia has historically had a tightly regulated telecom and financial services sector, with the state maintaining control over key sectors. Although the country has begun opening up to foreign investment, navigating regulatory frameworks and ensuring compliance with local laws can be challenging. Licensing and Policy Delays: The Ethiopian government recently started liberalizing its telecom sector, granting Safaricom Ethiopia a license in 2021. However, delays or complexities in acquiring mobile money licenses, adjusting to new fintech regulations, and securing approvals for cross-border services could slow down expansion plans.
2. Competition from Ethio Telecom’s Telebirr Local Competition: Ethio Telecom, the state-owned telecom company, has already launched its mobile money platform Telebirr, which has gained significant traction in the local market. Competing with an entrenched player backed by the government will require Safaricom to differentiate its services and offer compelling value propositions. Customer Loyalty: Convincing Ethiopians to switch from a well-known local brand to M-PESA may be difficult, particularly in a market where trust in financial services is still being cultivated.
3. Low Mobile Money Penetration Financial Literacy and Trust: Ethiopia has relatively low mobile money penetration compared to other African nations. Many people rely on cash transactions and may not be fully familiar with mobile money systems. Building trust and educating users about the benefits of mobile money, especially for cross-border transactions, will be crucial. Slow Adoption in Rural Areas: A significant portion of Ethiopia’s population resides in rural areas where digital and financial literacy may be lower. Reaching and onboarding these populations will require extensive marketing, awareness campaigns, and potentially partnerships with local organizations.
4. Infrastructure Challenges Limited Mobile and Internet Penetration: Although Ethiopia is rapidly improving its telecom infrastructure, many areas still lack reliable mobile and internet access. Poor network coverage in rural regions may hinder widespread adoption of mobile money services. Digital Infrastructure: Safaricom will need to invest in robust infrastructure to ensure smooth operations, secure transactions, and the capacity to handle increasing demand, especially as the service expands beyond major cities.
5. Currency and Transactional Barriers Foreign Exchange Controls: Ethiopia has strict foreign exchange controls, and fluctuating exchange rates could pose challenges for cross-border transfers. Safaricom may face difficulties managing currency conversions and ensuring that cross-border transactions are cost-effective for users. Cost of Remittances: Although M-PESA is known for its affordability, remittance fees and conversion costs could still pose barriers for lower-income Ethiopians who rely on remittances from abroad.
6. Cultural and Behavioral Barriers Resistance to Digital Financial Systems: In some communities, there may be resistance to adopting mobile money services, particularly where cash transactions are deeply ingrained in cultural practices. Safaricom will need to work to build trust and change behavior, showing that mobile money is safe, reliable, and convenient. Linguistic and Cultural Adaptation: Ethiopia is a linguistically diverse country with several ethnic groups. Safaricom may need to tailor its services to cater to various languages and cultural preferences, ensuring that marketing and customer support are accessible to all.
7. Security Concerns Cybersecurity and Fraud: As mobile money services grow, they often become targets for cyberattacks, fraud, and financial scams. Safaricom will need to implement strong security measures and fraud detection systems to protect users from financial risks, ensuring the integrity of the platform.
Regulatory Security Standards: Safaricom will also need to comply with Ethiopia’s security and data protection standards, ensuring that customer data and transactions are safeguarded, while aligning with international standards for digital financial services. Conclusion: The expansion of M-PESA Global into Ethiopia is a bold move with the potential to transform the country’s financial landscape, increase cross-border trade, and drive financial inclusion. However, Safaricom must overcome these significant challenges, including regulatory barriers, local competition, infrastructure limitations, and cultural hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges will determine the long-term success of the service in Ethiopia, while opening the door to broader regional growth.
Keywords:Safaricom M-PESA Global: Ethiopia mobile money challenges: Telebirr competition: Cross-border financial services: Digital financial inclusion
Technology
Kenya & Mauritius Lead East Africa’s Cybercrime Battle

: Kenya and Mauritius face rising DDoS attacks, topping East Africa. Discover
what drives these threats and how nations are fortifying defences.
Kenya and Mauritius are increasingly becoming hotspots for cybercrime in East Africa,
according to the recently released NETSCOUT 1H2024 DDoS Threat Intelligence
Report (TIR).
Both countries recorded the highest volumes of Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
attacks in the region, with cybercriminals deploying increasingly sophisticated, multi-
vector techniques to disrupt services.
DDoS SURGE IN KENYA AND MAURITIUS
Bryan Hamman, Regional Director for Africa at NETSCOUT, emphasised the growing
threat.
“Kenya and Mauritius are bearing the brunt of DDoS attacks in East Africa. Attackers
are not only increasing the volume but also leveraging multi-vector approaches that
make detection and mitigation far more challenging,” Hamman explained.
In Kenya, where the tech ecosystem thrives on innovations such as M-Pesa and
expansive mobile banking services, the Communications Authority of Kenya (CA)
reported a 12% increase in cyberattacks in the first half of 2024, translating to 459
million incidents.
Similarly, Mauritius, recognised as a financial hub, saw a sharp rise in attacks on its
financial services sector, a key contributor to its GDP.
WHAT DRIVES THE TARGETTING OF KENYA AND MAURITIUS?
Technological Advancement:
Both nations are at the forefront of digital transformation in East Africa, which,
while driving economic growth, also exposes vulnerabilities. Hamman noted,
“The more interconnected these economies become, the larger the attack
surface for cybercriminals.”
Economic Significance:
Kenya’s dominance as a regional tech hub and Mauritius’s role in global financial
services make them prime targets for malicious actors seeking to exploit high-
value systems.
Insufficient Cybersecurity Infrastructure:
Despite advancements, gaps in cybersecurity frameworks persist. For instance,
Kenya’s Data Protection Act of 2019 and Mauritius’s cybersecurity strategy have
struggled to keep pace with the sophistication of modern cyber threats.
COMPARISON WITHIN EAST AFRICA
While Kenya and Mauritius grapple with these challenges, regional peers like Rwanda
and Tanzania have demonstrated resilience.
- ● Rwanda: Known for its proactive measures, such as the National Cyber Security
- Authority (NCSA), Rwanda has kept DDoS incidents relatively low. In the first half
- of 2024, the country reported only 36 million attacks.
- ● Tanzania: With the establishment of its Computer Emergency Response Team
- (CERT) in 2020, Tanzania has reduced phishing and ransomware incidents by
- 35% and 20%, respectively.
IMPACT OF CYBERCRIME

The repercussions are severe, affecting sectors critical to economic stability:
● Kenya: The banking and telecommunications sectors, central to the country’s
GDP, have faced significant disruptions. Safaricom reported a two-hour outage in
April 2024 linked to a DDoS attack, costing millions in lost revenue.
● Mauritius: The financial services industry has suffered data breaches and
operational downtimes, undermining investor confidence.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ACTION
Enhanced Cybersecurity Policies:
Governments must update regulations to reflect evolving threats. Public-private
partnerships can also drive innovation in defence mechanisms.
Regional Collaboration:
Establishing an East African Cyber Defense Alliance could enable nations to
share threat intelligence and resources.
Investment in Education and Awareness:
Cyber hygiene training for individuals and businesses can help minimize
vulnerabilities, particularly against phishing attacks and social engineering
tactics.
Adoption of Advanced Technologies:
Leveraging tools like AI-driven threat detection can provide real-time responses
to attacks.
CONCLUSION
As cybercriminals grow bolder and more sophisticated, Kenya and Mauritius must
accelerate efforts to fortify their defences. “A regional approach that blends technology,
policy, and awareness is key to turning the tide against these threats,” Hamman
concluded.
The path forward is clear: a united East African front, coupled with robust internal
reforms, can transform the region from a target to a cybersecurity stronghold.
Technology
MTN Uganda Reports 29.6% Profit Rise to Shs 459.4bn in 2024
MTN Uganda’s revenue from mobile data and MoMo services jumped over 20% year-on-year, driven by growing demand for digital financial solutions and a strong focus on expanding MoMo’s reach.

: MTN Uganda’s profit climbs by 29.6% to Shs 459.4bn for 2024’s first nine months, driven by digital growth, fintech, and network expansion strategies.
MTN Uganda reported a 29.6% increase in profit after tax, reaching Shs 459.4 billion for the first nine months of the year, compared to Shs 354.5 billion during the same period in 2023.
This growth reflects the telecom giant’s strategic focus on expanding digital services and enhancing network coverage to capture more market share in Uganda’s competitive telecommunications sector.
CEO Cites Strategic Expansion and Digital Focus
Chief Executive Officer Sylvia Mulinge attributed the profit jump to effective cost management and a strong emphasis on digital transformation.
“Our increased investment in infrastructure and focus on digital financial services continue to yield positive results, as seen in this remarkable growth,” she stated during the earnings release.
Fintech and Data Services Lead Revenue Growth
Mobile data and MTN Mobile Money (MoMo) services played a significant role, as revenue from these segments has grown by over 20% year-on-year.
With Uganda’s demand for digital financial solutions rapidly increasing, MTN Uganda’s focus on expanding MoMo has led to a substantial boost in customer uptake, contributing to a large portion of this year’s growth.
Investments in Network Infrastructure Pay Off
MTN Uganda’s ongoing investments in 4G and 5G network infrastructure have also proven profitable.
In 2024, the company increased its capital expenditure to Shs 200 billion, up from Shs 160 billion in 2023, to meet the growing demand for faster and more reliable internet. “MTN Uganda has successfully captured the increased demand for reliable and faster internet,” said Henry Tumusiime, a telecom analyst based in Kampala. “Their proactive approach to enhancing data service capabilities has kept them ahead, especially as the economy becomes more digitised.”
Youth-Focused Campaigns Expand Subscriber Base
MTN’s early 2024 campaign aimed at youth — offering affordable data bundles and free educational content — attracted over 500,000 new users, expanding its subscriber base to 17 million, up from 16.5 million in 2023. This campaign has been instrumental in further driving revenue growth.
Outlook: Commitment to Quality and Digital Inclusion
Looking forward, MTN Uganda remains focused on delivering high-quality, affordable services to enhance digital inclusion. “As we approach year-end, our strategy remains anchored on delivering quality service, ensuring affordability, and growing digital inclusion,” Mulinge added.
MTN Uganda’s performance aligns with MTN Group’s broader strategy to connect Africa and strengthen digital finance solutions across the continent.
Technology
Skyleader 600 Launch in Tanzania: Boosting Local Aircraft Manufacturing
The Skyleader 600 marks a pivotal moment for Tanzania, not only in aviation but in its broader industrial aspirations.
With its maiden landing at Julius Nyerere International Airport, the aircraft stands as a symbol of Tanzania’s growing capacity to innovate, manufacture, and compete on the global stage.
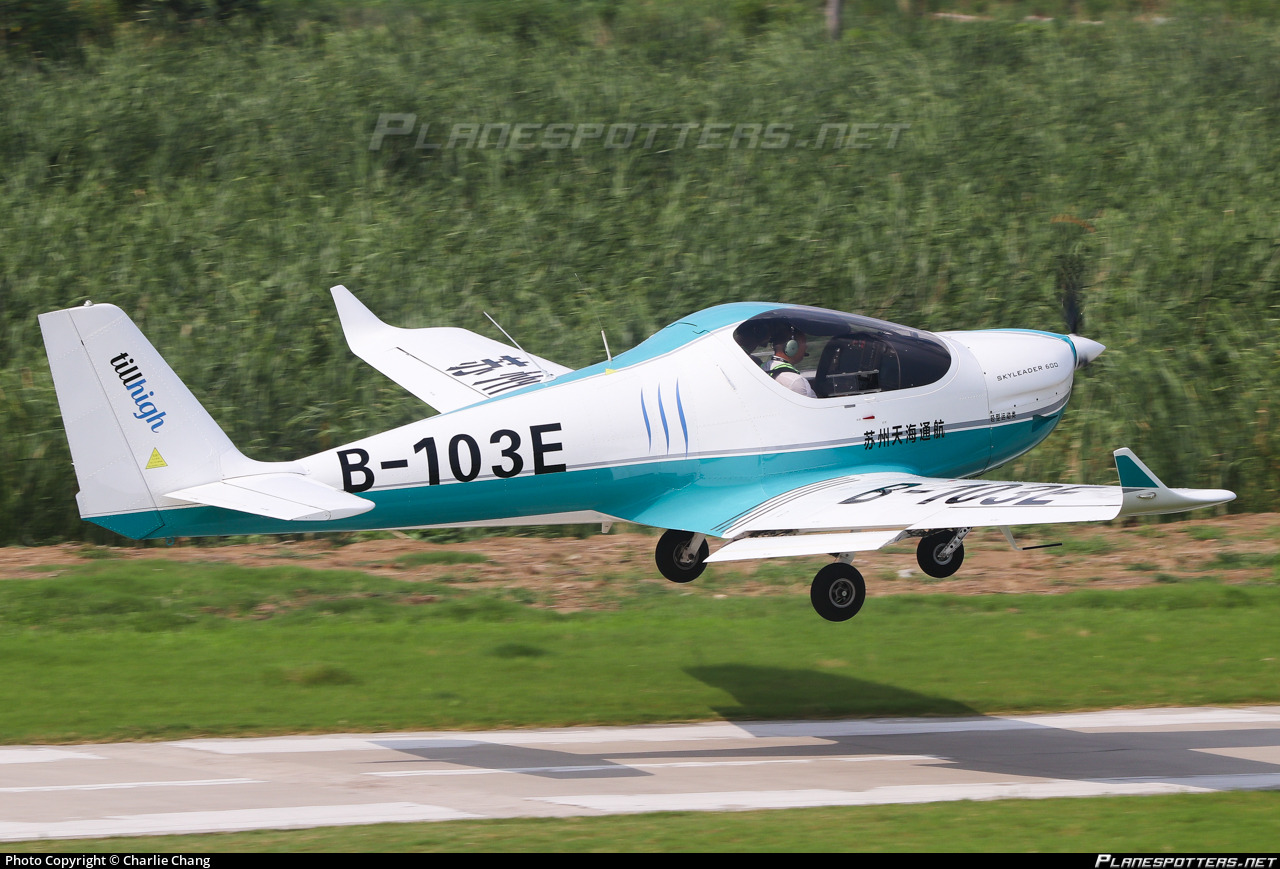

Discover Tanzania’s aviation breakthrough with the Skyleader 600, the first locally manufactured ultralight aircraft, unveiled at TIMEXPO 2024 in Dar es Salaam
By Charles Wachira
In a groundbreaking achievement for Tanzania and Africa’s aviation sector, AIRPLANE Africa Limited (AAL), based in Morogoro, launched the Skyleader 600, marking the first ultralight aircraft manufactured in the country.
The official unveiling took place at TIMEXPO 2024 in October 2024, setting a new milestone for local manufacturing and economic potential.
The Skyleader 600: A Game-Changer in African Aviation Designed with business travelers in mind, the Skyleader 600 can carry two passengers, offering a cost-effective alternative for long-distance travel.
The aircraft is praised for its modern design, affordability, and low maintenance costs.
Powered by petrol fuel, it addresses the growing demand for accessible and efficient transportation across Tanzania and the wider African market.
AAL’s Director, David Grolig, proudly remarked at the launch, “This is a historic moment not just for AIRPLANE Africa Limited, but for Tanzania. We have built something that will change the way people travel in this country and beyond.”
His statement reflects the company’s larger vision to transform Tanzania into a key player in ultralight aircraft manufacturing in Africa.
From Morogoro to the Skies: AAL’s Journey The journey to the Skyleader 600 began in 2019, when AIRPLANE Africa Limited was established in Morogoro.
The company blended local Tanzanian expertise with Czech aviation technology, a country renowned for its ultralight aircraft production.
This strategic collaboration has fostered a new generation of Tanzanian aviation professionals, thanks to internships and training programs designed to enhance skills and create jobs.
“The partnership with Czech aviation experts was crucial,” said Grolig. “It’s a blend of global expertise and local ambition. We’re showing that when we work together, we can achieve remarkable things.”
This combination has allowed AAL to tailor the Skyleader 600 to meet the unique needs of Africa’s business and private aviation sectors.
TIMEXPO 2024: Showcasing Tanzanian Innovation The TIMEXPO 2024 trade fair in Dar es Salaam served as the launch platform for the Skyleader 600.
This event, which highlights Tanzanian manufacturing, drew attention from global exhibitors and dignitaries.
The Minister for Industry and Trade was in attendance, noting the significance of AAL’s achievement: “This is a symbol of what we can achieve when we invest in our local industries. The government is committed to supporting such initiatives as they create jobs, foster innovation, and help us become more self-reliant.”
The launch has bolstered Tanzania’s image as a country capable of innovation, especially in high-tech sectors like aviation.
The Skyleader 600 is expected to open new economic opportunities in tourism, pilot training, and aircraft maintenance services.
Government Support and Economic Impact The Tanzanian government’s collaboration with AIRPLANE Africa Limited and its European partners has been key to the success of the Skyleader 600.
Support from regulatory authorities and the provision of trade incentives reflect the government’s commitment to fostering local industries that reduce reliance on imports.
Grolig acknowledged the government’s role, stating, “We couldn’t have done this without their backing. The government’s support has been essential in moving from concept to reality.”
This partnership is a model for public-private collaboration, particularly in industries like aviation that require significant investment and expertise.
Economic Potential and Future Growth The Skyleader 600’s production is expected to create ripple effects across Tanzania’s economy, from aviation services to job creation.
It provides an affordable transportation solution, not only for Tanzania but also for neighboring African markets.
AAL has ambitious plans to commercially sell the Skyleader 600, with Grolig hinting at future developments: “This is just the start. We plan to expand production, develop new models, and make Tanzania a leader in ultralight aircraft manufacturing in Africa.”
A Vision for the Future The Skyleader 600 represents a turning point for Tanzania, not just in aviation but in its broader industrial ambitions.
As the aircraft begins operations after its maiden landing at Julius Nyerere International Airport, it symbolizes Tanzania’s potential to innovate, manufacture, and compete on the global stage.
In a world where aviation is dominated by Western and Asian manufacturers, Tanzania, through AIRPLANE Africa Limited, is making its mark with the Skyleader 600—an ultralight aircraft that carries the hopes of a nation into the skies. Keywords: Skyleader 600 launch Tanzania ultralight aircraft manufacturing in Africa AIRPLANE Africa Limited TIMEXPO 2024 aviation showcase Tanzanian aviation industry growth
Keywords:Skyleader 600 launch Tanzania:Ultralight aircraft manufacturing in Africa: AIRPLANE Africa Limited:TIMEXPO 2024 aviation showcase:Tanzanian aviation industry growth
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoFred Okengo Matiang’i vs. President William Ruto: A 2027 Election Showdown
-

 Business & Money10 months ago
Business & Money10 months agoEquity Group Announces Kshs 15.1 Billion Dividend Amid Strong Performance
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoIchung’wah Faces Mt. Kenya Backlash Over Gachagua Impeachment Support
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoPresident Ruto’s Bold Cabinet Dismissal Sparks Hope for Change
-

 Politics7 months ago
Politics7 months agoPresident Ruto’s Lavish Spending Amid Kenya’s Economic Struggles Sparks Outrage
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoJohn Mbadi Takes Over Kenya’s Treasury: Challenges Ahead
-

 Business & Money2 months ago
Business & Money2 months agoMeet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?
-
 Politics7 months ago
Politics7 months agoKenya Grapples with Investor Confidence Crisis Amid Tax Protest Fallout





