Politics
Top 10 Richest Politicians in Sub-Saharan Africa 2024

: Discover the wealth and business ventures of Sub-Saharan Africa’s top 10
richest politicians in 2024, including details on their net worth and sources of
wealth.
Here’s the refined and ranked list of the richest politicians in Sub-Saharan Africa for
2024, starting with the wealthiest:
Table of contents
- 1–King Mohammed VI (Morocco)
- 2- Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo (Equatorial Guinea)
- 3–Yoweri Museveni (Uganda)
- 4- Ali Bongo Ondimba (Gabon)
- 5-Orji Uzor Kalu (Nigeria)
- 6 -Cyril Ramaphosa (South Africa)
- 7—Uhuru Kenyatta (Kenya)
- 8—Rochas Okorocha (Nigeria)
- 9—Mohammed Indimi (Nigeria)
- 10—Alassane Ouattara (Ivory Coast)
1–King Mohammed VI (Morocco)
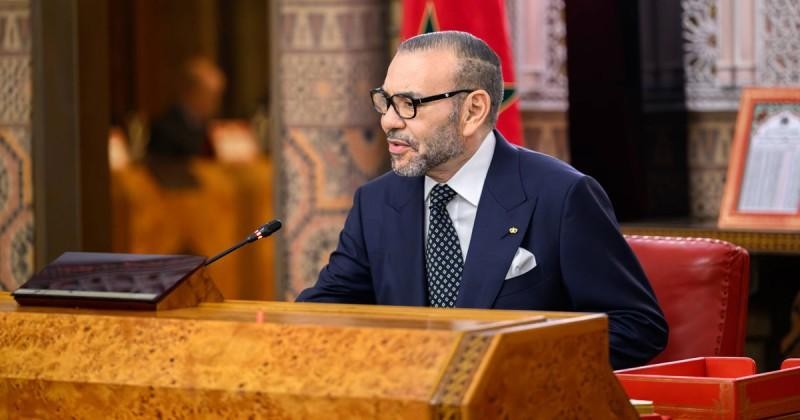

–Net worth: $1.9 billion
-Sources of Wealth: Royal investments across various sectors, including real estate, banking, and mining.
King Mohammed VI of Morocco: A Visionary Leader Shaping Morocco’s Future
King Mohammed VI, who ascended to the throne in 1999, has been a
transformative figure in Morocco’s modern history.
Under his leadership, Morocco has seen remarkable political, economic, and social reforms. His vision of modernisation, epitomised by the 2011 constitutional reforms, aimed to
strengthen democratic institutions and address the demands of the people.
King Mohammed VI has spearheaded ambitious projects, such as the development of
large-scale infrastructure, renewable energy initiatives, and the promotion of
Morocco as a regional economic hub.
His progressive approach continues to foster growth, stability, and Morocco’s growing influence on the African continent and beyond.
2- Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo (Equatorial Guinea)

-Net worth: $600 million to $1 billion
-Sources of Wealth: Oil and gas industry, with significant control over the
country’s resources.
Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo: Africa’s Longest-Serving Leader Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo, who has ruled Equatorial Guinea since 1979, is Africa’s longest-serving president. Coming to power after a military coup that ousted his uncle, Obiang’s tenure has been marked by significant oil wealth but also by criticisms of human rights abuses and political repression. While his regime has overseen.
economic growth fueled by oil exports, much of the wealth has remained concentrated
in the hands of the elite, with widespread poverty persisting. Despite facing international
scrutiny, Obiang has remained a key figure in Central African politics, navigating
relations with both Western powers and regional neighbours.
His leadership continues to shape the future of Equatorial Guinea, balancing development ambitions with ongoing calls for democratic reforms.
3–Yoweri Museveni (Uganda)

-Net worth: $1 billion
-Sources of Wealth: Diversified investments in agriculture, real estate, and
Uganda’s emerging oil industry.
Yoweri Museveni: A Pillar of Ugandan Politics for Over Three Decades
Yoweri Museveni, Uganda’s president since 1986, has been a dominant figure in the
country’s political landscape for over three decades.
Rising to power after leading a successful guerrilla war, Museveni promised to bring stability and economic growth to a nation that had been ravaged by dictatorship and civil conflict. Under his leadership, Uganda has experienced notable economic progress, particularly in agriculture and infrastructure.
However, his extended rule has also drawn criticism for democratic backsliding, with concerns over electoral fairness, media freedom, and human rights.
Despite calls for reform, Museveni remains a key player in East African geopolitics,
maintaining a strong influence on regional security and economic cooperation.
4- Ali Bongo Ondimba (Gabon)

-Net worth: $1 billion
-Sources of Wealth: Oil and state-controlled business ventures in Gabon.
Ali Bongo Ondimba: A Legacy of Leadership in Gabon Ali Bongo Ondimba, who served as president of Gabon from 2009 until his recent ousting in 2023, inherited leadership from his father, Omar Bongo, who ruled for over 40 years.
Ali Bongo’s presidency was marked by efforts to modernize the country’s
infrastructure, diversify its economy beyond oil, and implement social reforms. However,
his tenure was also characterized by growing concerns over political opposition
suppression, allegations of electoral fraud, and challenges to democratic governance.
Despite these controversies, Bongo remained a prominent figure in African politics, with a focus on regional cooperation and Gabon’s role in the international arena. His sudden
removal in a military coup has left a significant mark on Gabon’s future direction.
5-Orji Uzor Kalu (Nigeria)

Net worth: $1.1 billion
Sources of Wealth: Oil, banking, media, and real estate.
Orji Uzor Kalu: A Prominent Nigerian Politician and Business Mogul Orji Uzor Kalu, a key figure in Nigerian politics and business, has played a significant role in shaping the country’s political and economic landscape.
As the former governor of Abia State from 1999 to 2007, Kalu was known for his ambitious infrastructure projects and efforts to promote local industry. Beyond politics, he is a successful
businessman with interests spanning media, shipping, and manufacturing.
A member of Nigeria’s Senate since 2019, Kalu remains a powerful figure in the All Progressives Congress (APC), influencing national policy. Despite facing legal challenges in the past, including a corruption conviction that was later overturned, his influence continues to shape Nigeria’s political discourse.
6 -Cyril Ramaphosa (South Africa)

-Net worth: $450 million to $550 million
-Sources of Wealth: Mining, agriculture, and real estate, including his stake in
South Africa’s mining industry
Cyril Ramaphosa: Leading South Africa Through Challenges and Change Cyril Ramaphosa, South Africa’s president since 2018, has steered the country through a period of significant economic and political challenges.
Known for his role in the anti- apartheid struggle and as a key negotiator during the transition to democracy, Ramaphosa’s presidency has focused on tackling corruption, revitalising the economy, and addressing issues like unemployment and inequality.
Under his leadership, South Africa has also taken bold steps toward energy reform, including efforts to address the nation’s power crisis. Ramaphosa continues to be a central figure in the fight for a more inclusive and prosperous South Africa, despite facing both progress and setbacks during his tenure.
7—Uhuru Kenyatta (Kenya)
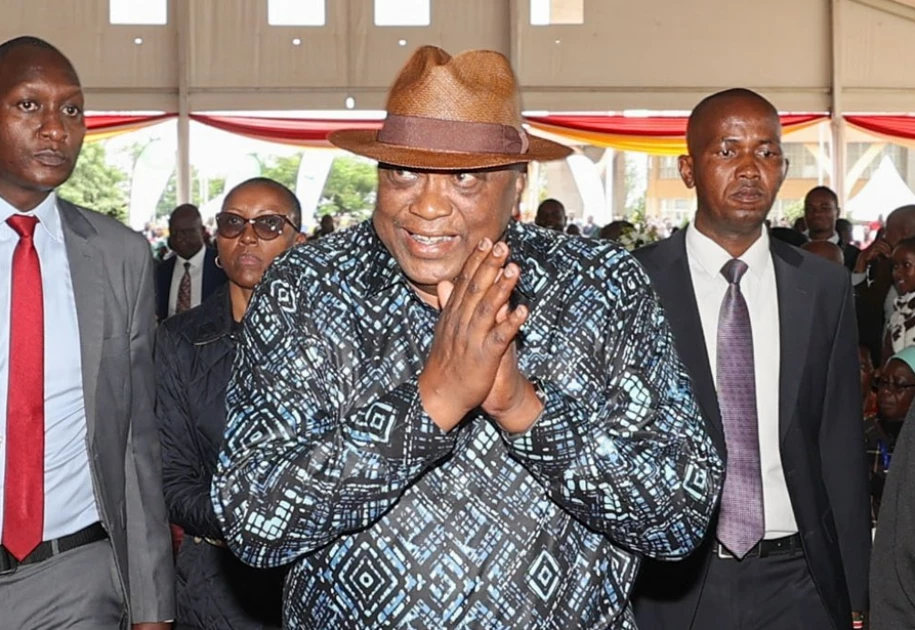

Net worth: $500 million to $650 million
Sources of Wealth: Family businesses in agriculture, banking (Brookside Dairy,
Commercial Bank of Africa), and real estate.
Uhuru Kenyatta: A Legacy of Leadership and Transformation in Kenya
Uhuru Kenyatta, Kenya’s president from 2013 to 2022, played a pivotal role in shaping
the nation’s political and economic landscape.
As the son of Kenya’s first president, Jomo Kenyatta, he navigated his leadership with a focus on infrastructure development, economic growth, and regional influence. During his two terms, Kenyatta spearheaded initiatives such as the Big Four Agenda, aimed at enhancing affordable housing, universal healthcare, manufacturing, and food security.
He also championed Kenya’s role in regional diplomacy and continental integration. Despite facing challenges, including the aftermath of political divisions and corruption scandals, Kenyatta remains a key figure in Kenya’s modern history, influencing both national and regional development.
8—Rochas Okorocha (Nigeria)
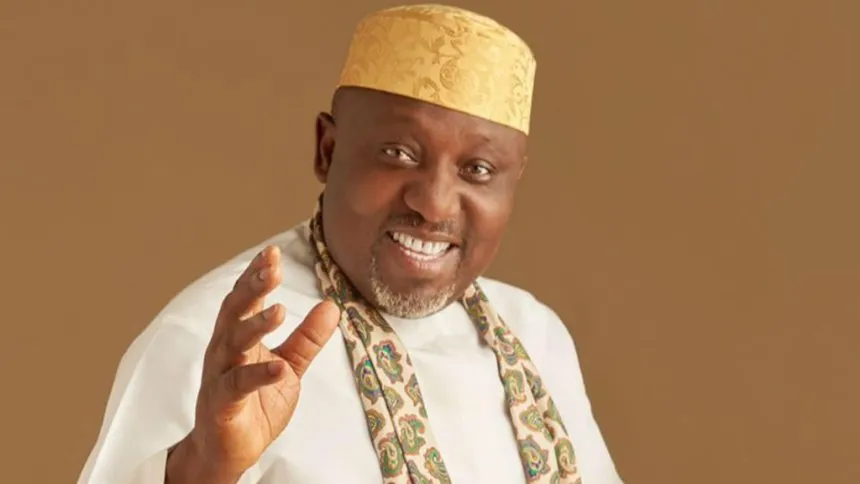

-Net worth: $1 billion
-Sources of Wealth: Education, media, real estate, and oil.
Rochas Okorocha: A Visionary Politician and Philanthropist in Nigeria Rochas Okorocha, former governor of Imo State, Nigeria, has made his mark as both a politician and philanthropist. Serving from 2011 to 2019, Okorocha focused on large-
scale infrastructure projects, educational reforms, and poverty alleviation, earning a
reputation for ambitious development plans.
Known for his larger-than-life personality and controversial policies, he also established numerous schools and institutions through his philanthropic work. A member of the All Progressives Congress (APC), Okorocha remains a key figure in Nigerian politics, continuing to influence both his state and national political discourse.
Despite facing challenges, including allegations of corruption, his legacy of public service and ambition shapes his ongoing political career.
9—Mohammed Indimi (Nigeria)

-Net worth: $1 billion. -Sources of Wealth: Oil and gas through his company, Oriental Energy Resources
Mohammed Indimi: A Nigerian Oil Tycoon and Business Mogul Mohammed Indimi is a prominent Nigerian businessman and one of the country’s wealthiest individuals, best known for his successful ventures in the oil and gas sector.
As the founder of the Oriental Energy Resources, Indimi has played a key role in
Nigeria’s oil industry, with a focus on exploration and production in the Niger Delta.
Beyond oil, he has diversified his interests into real estate, banking, and agriculture.
A philanthropist, Indimi is also recognised for his charitable work, particularly in education
and healthcare, through the Mohammed Indimi Foundation. His influence extends
across both business and political spheres, making him a significant figure in Nigeria’s
economic landscape.
10—Alassane Ouattara (Ivory Coast)
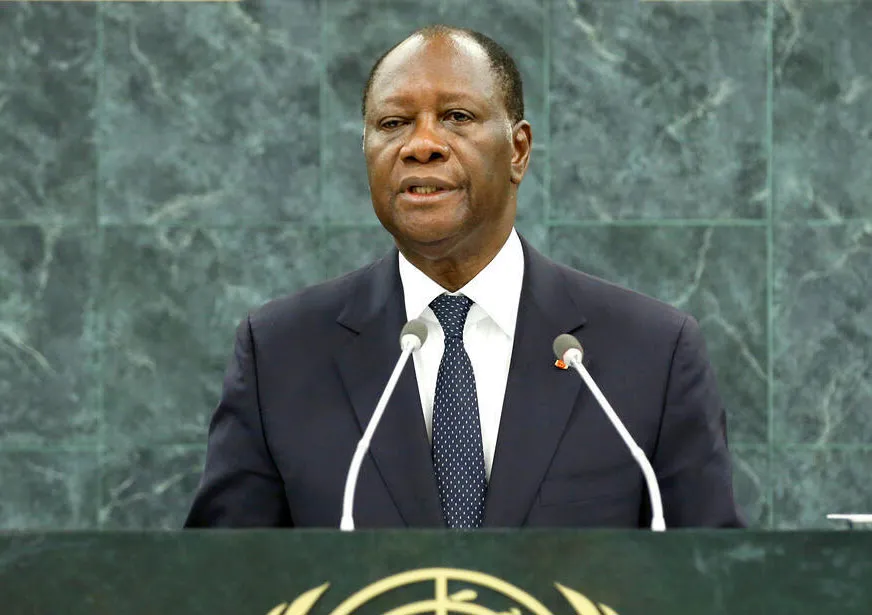

-Net worth: $500 million
-Sources of Wealth: Banking and finance, with substantial fortune accumulated in
the banking sector.
Alassane Ouattara: Steering Ivory Coast Towards Stability and Growth Alassane Ouattara, the president of Ivory Coast since 2011, has been a central figure in the country’s post-crisis recovery and economic transformation.
Taking office after a period of political unrest, Ouattara’s leadership has focused on restoring stability, attracting foreign investment, and driving economic growth. Under his administration, Ivory Coast has seen significant infrastructure development, a boost in agricultural exports, and improvements in education and healthcare.
Despite challenges, including political opposition and regional security concerns, Ouattara’s commitment to economic reform and national unity has solidified his position as a key leader in West Africa.
His tenure continues to shape the future trajectory of Ivory Coast, positioning the country as
a rising power on the African continent.
This ranking is based on a combination of publicly available data, business interests,
and political roles. These leaders have significantly diversified their wealth into
industries like oil, mining, real estate, and finance, often leveraging their political
influence for business growth.
Politics
William Ruto’s First Year: Promises Made, Struggles Persist
President Ruto cannot fulfil his manifesto unless he curbs runaway corruption and holds culprits accountable. The rule of law requires recovering proceeds of crime and prosecuting offenders for economic sabotage. This strategy would reduce the need to overburden Kenyans with taxes and additional borrowing.
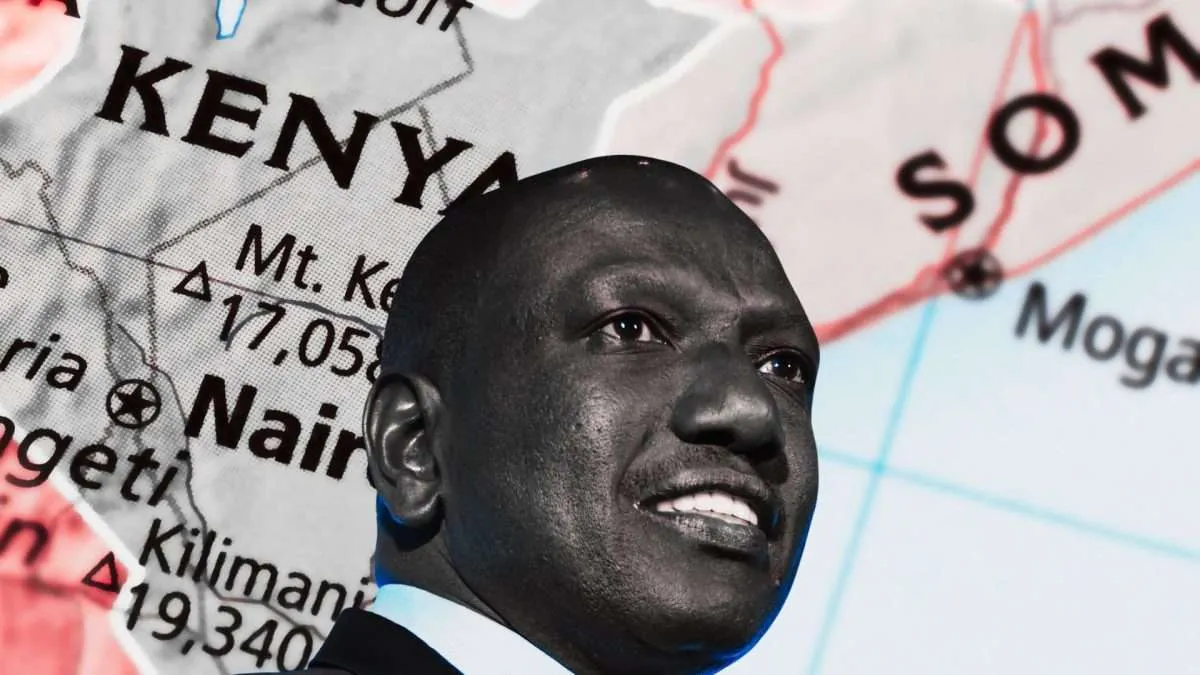

: Kenya’s President William Ruto faces challenges in fulfilling promises on governance, the economy, and national cohesion. Can he turn things around before 2027?
It’s more than a year since President William Ruto was sworn into office as Kenya’s fifth president.
He took office during a period of rising food and fuel prices, high unemployment, and a troubling debt burden in Kenya.
During the election campaign, Ruto promised to fix an economy afflicted by corruption and ineptitude. He promised to entrench good governance and place the poor at the centre of economic policy.
He pledged to address ethnicised politics and to uphold constitutionalism and the rule of law.
Ruto’s promises were significant. The rule of law and constitutionalism are key to economic planning and development, governance and equitable sharing of national resources.
They are the guardrails against impunity, democratic backsliding, lawlessness and political instability.
Throughout Kenya’s postcolonial period, the political elite have exploited ethnicity to obtain power at the expense of the collective well-being and social cohesion.
Elite entitlement has also weakened state institutions, leading to corruption and impunity.
I have studied democratic transitions, conflict and state building and elections in Africa.
My 2018 book examined how the political class had exploited ethnicity for political and economic advantage, resulting in weak and even dysfunctional state institutions in Kenya.
In his election campaign, Ruto identified the major issues that required urgent attention.
He addressed issues that needed swift action without constitutional changes, such as thawing the tension between the executive and the judiciary, decoupling the police finances from the executive, and taking port operations back to the coastal city of Mombasa from the inland town of Naivasha.
But resolving Kenya’s economic hardships has proved a hard nut to crack, as his 9 November 2023 State of the Nation address acknowledged. Just over a year since he was sworn in, Ruto is no nearer to turning the Kenyan ship around.
ECONOMIC TURBULENCE
As a candidate, Ruto portrayed himself as an outsider to Kenya’s power matrix who was best placed to improve the living conditions of the poor and excluded. But the economy has not improved under his watch. If anything, living conditions have worsened.
The cost of living is higher after a steep increase in the petrol price and the local currency’s loss of value. Ruto’s government has imposed new and increased taxes on Kenyans, ostensibly to reduce or remove the need for external borrowing.
The government was quick to remove fuel and food subsidies but has been slow to address government wastage.
The government’s key strategy was to subsidise fertiliser to boost harvests and achieve food security. It remains to be seen whether this will happen.
More deliberate measures are required to turn around agriculture as the mainstay of the economy.
On the question of centring the poor and marginalised in governance, Ruto focused on the financial sector. The government rolled out the “Hustler Fund” to make credit more affordable.
But the fund’s impact on overall living standards through job creation, for instance, is likely to be cancelled out by a punitive tax regime and a struggling economy.
RULE OF LAW
Ruto’s first public event as president was to approve the appointment of six judges left in limbo by his predecessor, Uhuru Kenyatta. He also made good on his promise to allocate more funding to the judiciary.
However, to entrench the rule of law and constitutionalism calls for more than this. Judicial officers must act with utmost integrity. To affirm equality before the law, errant senior state officers and the political elite must face the law and if found guilty sanctioned decisively.
The Kenyan judiciary is still bedevilled by corruption that impedes access to justice. Disturbingly, it is seen as more inclined to punish the poor while letting the rich and political elite act with impunity.
Ruto himself has obeyed court rulings that went against him, unlike under Kenyatta, when disregard for the law was the norm. Critics, however, including the Law Society of Kenya, have accused his administration of disobeying court orders like his predecessor.
Ruto spoke out against extrajudicial and summary executions and enforced disappearances perfected by the police over the years.
He sought to accord the police financial and operational autonomy. Thus he transferred accounting for the police budget to the police as he had promised.
Despite these changes, a culture of impunity and lack of transparency continues to undermine the Kenyan police. Extrajudicial executions continue. The police must be placed under civilian oversight as envisaged under the constitution.
The failure to set up a commission of inquiry into state capture under his predecessor, as promised during campaigns, dented Ruto’s commitment to the fight against corruption. A year later, a commission of inquiry has not been formed and the issue seems to have been abandoned altogether.
It is unlikely that Ruto will fulfil his manifesto unless he reins in runaway corruption and the culprits are held to account.
The rule of law demands that proceeds of crime be recovered and offenders charged for economic sabotage. This approach would obviate the need to burden Kenyans with taxes and more borrowing.
NATIONAL COHESION
Appointments to government positions have been undermined by the age-old problems of recycling appointees, patronage, nepotism and ethnicity. Just as worrying are senior government officials publicly advancing exclusionary ethnic politics with impunity. Ruto must rein them in.
It is also a setback that Ruto acceded to talks to assuage the opposition elite who had resorted to violent protests against his historic victory. These elitist self-serving talks could lead to constitutional amendments creating more political positions under a cynically flawed logic that this approach enhances national cohesion.
This is an about-turn on Ruto’s part.
Ultimately national cohesion is Ruto’s pressing challenge.
Kenya is divided on many fronts – economic, ethnic, regional and religious – a legacy of previous governments.
Ruto needs to look beyond ethno-regional appointments. For legitimacy and transformation, he needs to ideologically reconnect with and dignify the “hustler nation”, the disenfranchised constituency that propelled him into power. Bar this, he could face an intensely contested reelection bid like his predecessors.
Politics
Rigathi Gachagua’s Impeachment: A Political Conundrum for Ruto’s Administration
Former Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua’s impeachment has transformed Kenya’s political landscape, marking the first event of its kind under the 2010 Constitution.
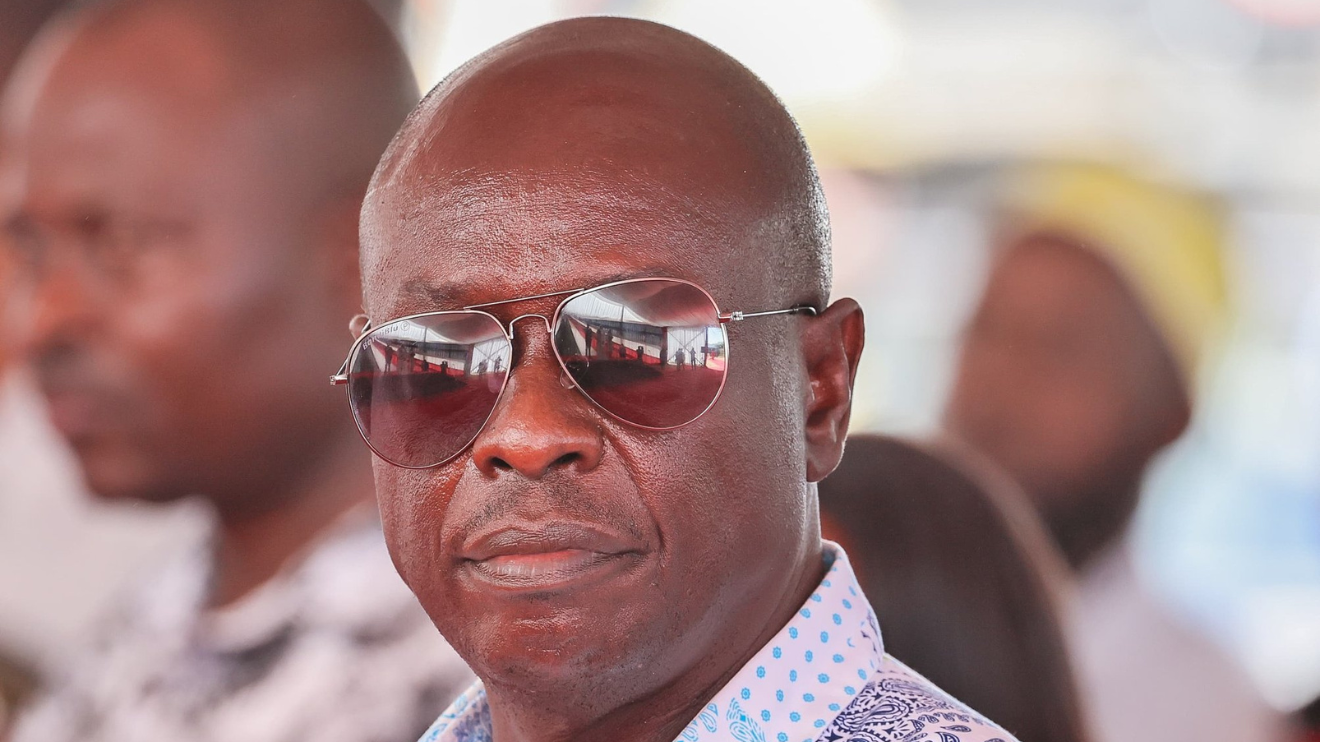

: Explore the political crisis after Rigathi Gachagua’s impeachment, its impact on William Ruto’s leadership, and the road to Kenya’s 2027 elections.
The impeachment of former Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua has upended Kenya’s political landscape, marking the first instance of such an event under the 2010 Constitution.
Accused of divisive politics and judicial interference, Gachagua’s ousting has ignited significant political tensions, particularly within the populous Mt. Kenya region, which has been a cornerstone of President William Ruto’s support base.
Gachagua has vocally criticised Ruto, describing his former ally as “vicious” and accusing him of orchestrating the impeachment.
In a fiery statement, Gachagua claimed, “The man I helped to become president has betrayed me,” while also alleging threats to his safety.
His impeachment has left the deputy presidency in limbo, with a court temporarily halting the appointment of Interior Minister Kithure Kindiki as his replacement.
Impact on Ruto’s Political Strategy
This political rift presents a dual challenge for Ruto. On one hand, it exposes cracks within the ruling coalition, with some legislators fearing backlash in their constituencies for supporting Gachagua’s removal.
On the other, it provides opposition leaders an opportunity to capitalise on perceived disunity within the government, potentially reshaping alliances as the 2027 elections approach.
Moreover, Gachagua’s removal has highlighted the volatile nature of Kenyan politics, where loyalty often shifts based on regional and ethnic dynamics.
Analysts believe Ruto must now tread carefully to maintain his hold over Mt. Kenya, a region critical to his electoral prospects.
The Way Forward
The administration must immediately stabilize governance by resolving the court dispute over Gachagua’s replacement or reconciling with dissenting factions.
Political analysts suggest that Ruto should focus on unifying his coalition and delivering tangible results to counter opposition narratives.
As Kenya moves closer to the 2027 polls, this episode underscores the importance of political cohesion and strategic messaging. Whether Ruto can overcome this challenge or face further fallout will significantly shape the country’s political trajectory.
Politics
Kenya Under Ruto: Transformative Leadership or Mounting Challenges?
Ruto’s policies have sparked mixed reactions on the social front. While he has taken a prominent role in addressing global challenges like climate change—evident in hosting a landmark summit that secured billions in clean energy investments—critics contend that his focus on international priorities has overshadowed pressing domestic concerns. Issues such as food insecurity and unemployment remain unresolved, leaving many Kenyans feeling neglected despite the administration’s ambitious global commitments.

: Analyse President William Ruto’s leadership in Kenya, focusing on economic reforms, political strategies, and social challenges shaping the nation’s future.
Kenya’s President William Ruto, in office since September 2022, has faced mixed reviews regarding his leadership, particularly on economic, political, and social fronts.
Bold reforms, mounting challenges, and a mixed reception among citizens have marked his administration.
Economic Landscape
Ruto inherited an economy grappling with high debt levels ($69 billion), inflation, and global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the Ukraine war.
Despite efforts to stabilise the economy, including introducing new taxes and eliminating fuel subsidies to secure loans from the IMF and World Bank, these measures have strained ordinary Kenyans.
Household essentials, including sugar and beans, saw price hikes up to 61% and 30%, respectively. Inflation moderated to 6.7% in August 2023, but economic growth is projected to be slower than the 4.8% recorded in 2022
.Key initiatives such as the “Hustler Fund,” aimed at empowering small-scale entrepreneurs, have not delivered the expected outcomes, with some analysts like Ken Gichinga calling Ruto’s economic policies “ineffective.”
However, Ruto has also promoted local manufacturing and reduced reliance on imports to support job creation.
.
Political Strategy
On the political front, Ruto has shown determination to fight corruption.
His administration has introduced measures to track government spending and eliminate payroll fraud through a Unified Personal Identification system.
He has also emphasised accountability, stating, “We shall levy a surcharge against any officer who causes a loss of public resources.” However, critics question the effectiveness of these reforms, especially in light of continued economic hardships
Ruto’s administration faced opposition-led protests over rising living costs, which turned deadly, leaving 50 people dead.
These tensions underscore the political divisions and challenges in delivering tangible benefits to Kenyans
.Social Impact
Socially, Ruto’s policies have had polarising effects. While he champions global issues like climate change, hosting a major summit that attracted billions in clean energy investments, critics argue that his focus on international engagements has left domestic issues, such as food insecurity and unemployment, unresolved.
Analysts like Nerima Wako-Ojiwa emphasise that many Kenyans are now struggling with basic needs like food, highlighting a disconnect between the administration’s priorities and grassroots realities
.Broader Context and Future
Ruto has positioned himself as a reformer, focusing on transparency and economic restructuring.
However, his administration faces the twin challenge of delivering immediate relief to struggling Kenyans while maintaining long-term fiscal responsibility.
Supporters like Joseph Mwiti argue that transformative policies take time to bear fruit, reflecting cautious optimism about Ruto’s leadership.
In sum, President Ruto’s tenure has been characterised by ambitious reforms and significant headwinds. The success of his administration will depend on balancing economic recovery, political stability, and social equity in the coming years.
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoFred Okengo Matiang’i vs. President William Ruto: A 2027 Election Showdown
-

 Business & Money10 months ago
Business & Money10 months agoEquity Group Announces Kshs 15.1 Billion Dividend Amid Strong Performance
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoIchung’wah Faces Mt. Kenya Backlash Over Gachagua Impeachment Support
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoPresident Ruto’s Bold Cabinet Dismissal Sparks Hope for Change
-

 Politics7 months ago
Politics7 months agoPresident Ruto’s Lavish Spending Amid Kenya’s Economic Struggles Sparks Outrage
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoJohn Mbadi Takes Over Kenya’s Treasury: Challenges Ahead
-

 Business & Money2 months ago
Business & Money2 months agoMeet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?
-
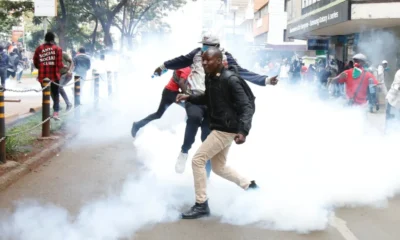
 Politics7 months ago
Politics7 months agoKenya Grapples with Investor Confidence Crisis Amid Tax Protest Fallout





