CLIMATE CAPITAL
Kenya Launches NBCM to Boost National Biodiversity Conservation
Kenya boasts a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna, featuring iconic species such as elephants, rhinos, and lions, as well as unique plants found nowhere else on the planet. However, the country is confronted with serious threats to its biodiversity. The Kenya National Bureau of Statistics reports that more than 50% of wildlife habitats are under significant pressure from agriculture, urbanization, and climate change. Therefore, the launch of the National Biodiversity Coordination Mechanism (NBCM) is timely, as it aims to implement proactive measures to address these challenges.

In a significant stride towards safeguarding its rich natural heritage, Kenya this August 2024 launched the National Biodiversity Coordination Mechanism (NBCM). This initiative aims to enhance the country’s conservation efforts and streamline the management of biodiversity resources across various sectors. As one of the most biodiverse nations in the world, Kenya recognizes that its wildlife and ecosystems are not only vital for environmental health but also crucial for the economy, tourism, and the livelihoods of millions of Kenyans.
Understanding the NBCM
The NBCM serves as a comprehensive framework to integrate biodiversity considerations into national policies and strategies. The mechanism will facilitate collaboration among government agencies, local communities, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other stakeholders to ensure a coordinated approach to biodiversity management. By creating a centralized system for monitoring and reporting on biodiversity-related activities, the NBCM is expected to improve the effectiveness of conservation initiatives while addressing the challenges posed by climate change, habitat destruction, and human-wildlife conflict.
During the launch, Festus Ng’eno, Principal Secretary at the Ministry of Environment, Climate Change, and Forestry, highlighted the crucial role of the National Biodiversity Coordination Mechanism in ensuring the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity for current and future generations.
“This mechanism is essential for supporting the implementation of our national and international commitments,” Ng’eno stated. “It aligns Kenya’s efforts with the goals of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which emphasizes the urgent need for action to address biodiversity threats and promote sustainable resource use by 2030.”
The new mechanism seeks to harmonize biodiversity conservation goals, policies, and practices across national, county, and community levels, ensuring a cohesive approach to safeguarding Kenya’s abundant natural resources. It will also serve as a vital tool for aligning the country’s strategies with key global conventions, including the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Dr. Erustus Kanga, Director-General of the Kenya Wildlife Service, emphasized the urgent need to tackle the unprecedented challenges currently threatening the country’s biodiversity.
“Climate change, habitat destruction, pollution, and the over-exploitation of natural resources pose significant threats to our biodiversity. This mechanism provides a strategic path for collaboration on solutions that will help mitigate these challenges and strengthen our conservation efforts,” Kanga stated.
The launch of the National Biodiversity Coordination Mechanism signifies a crucial step in Kenya’s dedication to biodiversity conservation. This platform fosters enhanced collaboration, strategic planning, and collective action aimed at safeguarding the country’s rich ecological heritage.
With this mechanism now operational, Kenya is well-positioned to make substantial progress toward the objectives outlined in the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. It ensures the sustainable management of natural resources while balancing environmental protection with the needs of its people.
The Context of Biodiversity in Kenya
Kenya is home to an astounding variety of flora and fauna, including iconic species such as elephants, rhinos, and lions, alongside unique plants found nowhere else on Earth. However, the country faces significant threats to its biodiversity. According to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics, over 50% of wildlife habitats are under pressure from agriculture, urbanization, and climate change. As such, the NBCM comes at a crucial time when proactive measures are needed to combat these pressures.
The launch of the NBCM is timely, coinciding with the United Nations’ Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2030), which emphasizes the urgent need to restore and protect ecosystems worldwide. Kenya’s commitment to these global efforts signals its determination to play a leading role in biodiversity conservation on the continent and beyond.
Community Involvement and Local Knowledge
One of the cornerstones of the NBCM is the recognition of the vital role local communities play in biodiversity conservation. Traditional knowledge and practices are crucial in managing natural resources sustainably. The NBCM will promote community engagement and empower local stakeholders, enabling them to participate actively in conservation efforts and decision-making processes.
“We cannot achieve our conservation goals without the involvement of local communities,” said Dr. Francis Karanja, the Director of the Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS). “Their knowledge, experience, and stewardship of the land are invaluable to our efforts.”
Challenges Ahead
While the NBCM represents a promising step forward, several challenges remain. Ensuring adequate funding, enforcing conservation laws, and addressing the underlying drivers of biodiversity loss, such as poverty and land-use change, will require sustained effort and collaboration. The Kenyan government, along with its partners, will need to advocate for more significant investments in conservation and sustainable development practices to turn the ambitions of the NBCM into tangible results.
Looking Forward
The establishment of the NBCM marks a watershed moment in Kenya’s conservation journey. As the country strives to balance development with ecological integrity, the NBCM could serve as a model for other nations facing similar challenges. By prioritizing biodiversity in national planning and fostering collaboration across sectors, Kenya has the potential to not only preserve its natural treasures but also enhance its resilience to climate change and foster sustainable livelihoods for its people.
“This is just the beginning,” concluded Ngeno. “We are committed to working together, with every stakeholder involved, to ensure that our biodiversity is preserved, protected, and celebrated.”
As Kenya embarks on this vital journey, the world watches with anticipation, hopeful that the NBCM will yield positive outcomes for its diverse ecosystems and the communities that depend on them.
Keywords:Kenya Biodiversity Conservation: National Biodiversity Coordination Mechanism: Ecosystem Management: Sustainable Resource Use: Community Engagement in Conservation
CLIMATE CAPITAL
Access Bank Secures CAK Approval for National Bank Acquisition

: Access Bank to acquire National Bank of Kenya for $100M, boosting market
share to 1.9% with CAK approval and workforce retention conditions.
CAK Approves Access Bank’s Acquisition of NBK with Conditions
The Competition Authority of Kenya (CAK) approved Access Bank’s acquisition of the
National Bank of Kenya (NBK) from KCB Group, requiring Access Bank to retain 80% of
NBK’s workforce for at least one year.
The Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) must now give its final approval for the deal.
Employment Retention Key to Approval
According to CAK, Access Bank must maintain 80% of NBK’s 1,384 employees and all
316 staff from its local subsidiary, Access Bank Kenya, for a year following the
transaction’s completion. “The transaction has been approved on condition that Access
Bank Plc retains, for one year, at least 80% of the target’s current workforce,” CAK
stated.
Deal Valuation and Finalization Timeline
While the deal’s value has not been disclosed, KCB Group announced in March 2024
that NBK would be sold for 1.25 times its book value. With NBK’s 2023 book value at
$79.77 million, the acquisition is estimated to be worth approximately $100 million. The
transaction is expected to conclude in November.
Expanding Access Bank’s Kenyan Presence
Access Bank’s current footprint in Kenya includes 23 branches in 12 counties. Acquiring
NBK’s 77 branches across 28 counties will significantly boost its presence and service
offerings, including retail, corporate, and Islamic banking. Access Bank, currently
ranked as a tier 3 lender, will integrate with NBK, a tier 2 institution, enhancing its status
in the market.
Market Share and Competition Analysis
The acquisition will give the merged entity a 1.9% market share in Kenya’s banking
sector. “The combined market size is unlikely to raise competition concerns since it is
low,” CAK noted. “The merged entity will face competition from other banks in the
market. Based on this, the transaction is unlikely to substantially lessen or prevent
competition.”
CLIMATE CAPITAL
Patricia Ithau: CEO of WPP-Scangroup, Leading Africa’s Marketing Giant

: She leads WPP-Scangroup PLC, the largest marketing and communication group in sub-Saharan Africa, driving innovation, business growth, and social impact across the region.
Patricia Ithau leads WPP-Scangroup PLC, the largest marketing and communication group in sub-Saharan Africa. She took over as CEO on March 14, 2022, succeeding Bharat Thakrar at the helm of this Nairobi Securities Exchange-listed company.
Under her visionary leadership, WPP-Scangroup continues to redefine the marketing and advertising landscape in East Africa through a multi-agency, multi-disciplinary approach.
Her focus on pushing the boundaries of creativity and innovation has positioned the company to drive growth and deliver groundbreaking solutions across the region.
Early Life and Academic Foundation
Patricia’s leadership journey grew from a strong academic foundation.
Patricia Ithau studied at Loreto Convent Msongari in Nairobi before earning her Bachelor of Commerce degree from the University of Nairobi.
Further expanding her knowledge, she earned an MBA in Strategic Management from the United States International University-Africa.
She also completed advanced management programs at prestigious institutions like Strathmore University, IESE Business School, INSEAD, and Oxford University, laying the foundation for a distinguished career in business leadership.
Career Milestones: L’Oréal Africa and Beyond
Before joining WPP-Scangroup, Patricia was the founding CEO of L’Oréal Africa, where she significantly drove the company’s growth and success in the region.
Under her leadership, L’Oréal’s African subsidiary generated $25 million in annual revenue, employed over 270 people, and produced 40 million units annually.
One of her key achievements was leading one of the first acquisitions of a local business by a multinational in East Africa, demonstrating her ability to drive growth and market penetration in the competitive FMCG sector.
Advocacy for Women in Leadership
Patricia has actively championed women in leadership, advocating for creating opportunities that allow women to thrive in the corporate world.
As an Ambassador for the Women on Boards Network (WOBN) in Kenya, she has worked to elevate women into leadership positions.
She holds board positions at organisations such as ABSA Bank Kenya, Jambojet Ltd, Vivo Fashion Group, and the British Chamber of Commerce.
Furthermore, Patricia actively supports corporate governance and social impact as a Trustee for the Vodafone Foundation (UK) and the M-PESA Foundation.
Overcoming Personal Challenges and Building Resilience
In addition to her professional achievements, Patricia’s journey has been marked by resilience.
She was crowned Miss Kenya in 1986 during her first year at the University of Nairobi.
Navigating societal judgments and stereotypes during this period helped shape her leadership abilities, teaching her invaluable lessons in self-confidence and perseverance.
Recognition and Awards
Patricia’s contributions to Kenya’s economic growth and development have not gone unnoticed.
In 2020, she was awarded the Head of State Commendation (HSC) for her outstanding role in business development.
Patricia is also an accredited executive coach and certified Emotional Intelligence practitioner, emphasising her commitment to fostering future leaders who embrace emotional intelligence and holistic leadership practices.
Corporate and Social Impact
Patricia’s leadership extends beyond the corporate world.
As East Africa Regional Director for the Stanford Institute for Innovation in Development Economies (SEED), Patricia has driven sustainable business growth and job creation across sub-Saharan Africa.
Through SEED, she has supported over 200 businesses in tackling leadership challenges and fostering innovation, contributing significantly to the region’s economic transformation.
Family and Personal Values
Patricia is also deeply committed to her family.
She proudly raises her two daughters, Mueni and Makena, instilling in them the values of hard work and resilience.
Her role as a mother aligns with her broader mission of mentoring and guiding the next generation of leaders.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Leadership and Innovation
Patricia Ithau leads with vision, innovation, and a strong commitment to social sustainability, from her strategic achievements at L’Oréal Africa to her current role as CEO of WPP-Scangroup.
Her dedication to advancing women in leadership, her contributions to the business community, and her efforts in developing future leaders make her a lasting influence on Africa’s corporate sector, inspiring and driving progress across the region.
CLIMATE CAPITAL
Meet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?

: The nomination speaks volumes about the bank’s commitment to its African operations and its strategic vision for growth on the continent.
: Kariuki’s vast experience and market insight make him a catalyst for growth. With his strategic vision, Standard Chartered can seize opportunities, expand, and provide tailored financial solutions
In a significant move within the banking sector, Kariuki Ngari ascended to CEO Africa at Standard Chartered Bank on April 3, marking a pivotal moment in his illustrious career. As he steps into this new role, Ngari faces a landscape rife with challenges but brimming with opportunities. He is poised to leverage his expertise and track record to propel the bank’s growth trajectory across Africa.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Navigating Regulatory Complexity: One of Kariuki’s foremost challenges will be navigating the diverse regulatory environments across the African continent. With each country presenting unique regulations and compliance requirements, Ngari must adopt a nuanced approach to ensure Standard Chartered Bank’s operations remain compliant while driving growth.
Adapting to Market Dynamics: African markets are diverse and constantly changing. Rapid shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and intense competition characterise them. Kariuki must stay agile and adaptive, seizing opportunities for innovation and market expansion while mitigating risks associated with changing market dynamics.
Fostering Financial Inclusion: Africa offers significant opportunities for financial inclusion, as a large portion of the population remains underserved by traditional banking services. Kariuki has the opportunity to drive initiatives that promote financial literacy, expand access to banking services, and foster inclusive economic growth across the continent.
Previous Achievements and Experience:
Before assuming the role of CEO of Africa, Kariuki served in various leadership positions within Standard Chartered Bank, demonstrating his exceptional leadership capabilities and strategic vision. Some of his notable achievements include:
Driving Digital Transformation: Kariuki played a pivotal role in driving Standard Chartered Bank’s digital transformation agenda, spearheading initiatives to enhance the bank’s digital capabilities and customer experience. Under his leadership, the bank successfully launched innovative digital banking solutions tailored to the African market, driving customer engagement and retention.
Expanding Market Presence: Kariuk has a proven track record of expanding Standard Chartered Bank’s market presence across Africa, identifying growth opportunities, and forging strategic partnerships to penetrate new markets and strengthen the bank’s foothold in existing ones.
Promoting Sustainable Finance: Kariuki is committed to promoting sustainable finance and responsible banking practices. He has championed initiatives focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles, integrating sustainability into the bank’s business strategy and operations.
Expectations in the New Role:
As CEO of Africa, stakeholders expect Kariuki to bring his wealth of experience, strategic acumen, and unwavering commitment to driving Standard Chartered Bank’s growth agenda in Africa. Key expectations include:
Strategic Vision: Kariuki will continue articulating a clear vision for Standard Chartered Bank’s African operations, leveraging market insights and industry trends to identify growth opportunities and drive sustainable value creation.
Innovation and Digitalization: Ngari will prioritise innovation and digitalisation, harnessing the power of technology to enhance the bank’s offerings, streamline operations, and deliver superior customer experiences.
Stakeholder Engagement: Ngari will intensely focus on stakeholder engagement, fostering relationships with clients, regulators, shareholders, and communities to ensure alignment with the bank’s objectives and values.
The nomination of Kariuki to the position of CEO of Standard Chartered Africa speaks volumes about the bank’s commitment to its African operations and its strategic vision for growth on the continent. Here are a few critical points that the nomination signifies:
Recognition of Talent: Standard Chartered Bank’s decision to appoint Kariuki Ngari as CEO of Africa reflects the bank’s recognition of his exceptional leadership qualities, strategic acumen, and track record of success within the organisation. It indicates that the bank values talent from within its ranks and is committed to nurturing and promoting internal talent to key leadership positions.
Focus on the African Market: By appointing a CEO specifically for the African region, Standard Chartered Bank underscores the importance of the African market in its global strategy. It signifies the bank’s commitment to unlocking the vast opportunities presented by the African continent and leveraging its potential for growth and expansion.
Continuity and Stability: Kariuki’s nomination brings continuity and stability to Standard Chartered Bank’s African operations. With his deep understanding of market dynamics, extensive experience within the organisation, and proven track record of success, Ngari is well-positioned to provide steady leadership and drive the bank’s growth agenda in Africa.
Emphasis on Local Leadership: The appointment of Kariuki, who is of Kenyan nationality, also highlights the importance of local leadership and expertise in driving success in the African market. It demonstrates Standard Chartered Bank’s commitment to fostering a diverse and inclusive leadership culture that reflects the communities and markets it serves.
Strategic Direction: Kariuki’s nomination signifies the bank’s strategic direction and priorities for its African operations. It suggests a focus on driving innovation, digital transformation, and sustainable growth in key markets across the continent, with Ngari leading the charge in executing the bank’s vision and objectives in Africa.
Kariuki’s appointment as CEO of Africa at Standard Chartered Bank marks a significant milestone in the institution’s journey towards consolidating its position as a premier financial institution on the African continent. With an unwavering focus on excellence, strategic foresight, and a proven track record of leadership, Kariuki brings a wealth of experience and expertise that positions him as a catalyst for transformative growth.
His elevation underscores the bank’s confidence in his abilities and its steadfast commitment to fostering homegrown talent and leveraging local expertise to drive success in key markets. Kariuki’s appointment represents more than just a change in leadership; it symbolises a new era of innovation, resilience, and adaptability in navigating the intricacies of the African financial landscape.
In the face of evolving market dynamics, regulatory complexities, and competitive pressures, Kariuki’s leadership will be instrumental in steering Standard Chartered Bank towards sustainable growth and value creation. His strategic vision, coupled with a deep understanding of the African market, will enable the bank to capitalise on emerging opportunities, expand its footprint, and deliver superior financial solutions tailored to the diverse needs of its customers.
Moreover, Kariuki’s appointment reinforces Standard Chartered Bank’s commitment to driving positive impact and fostering inclusive growth across the continent. Kariuki is poised to make a meaningful difference in millions of individuals and businesses across Africa by championing initiatives promoting financial inclusion, sustainability, and responsible banking practices.
In essence, Kariuki’s nomination heralds not just a new chapter but an entire volume in the bank’s narrative of success in Africa. It signifies a renewed sense of purpose, a reaffirmation of values, and a shared commitment to shaping a brighter future for the continent’s economies and communities. As he assumes the mantle of leadership, Ngari stands at the forefront of Standard Chartered Bank’s journey towards becoming the partner of choice for businesses, investors, and individuals alike, propelling Africa towards a future of prosperity and opportunity.
-

 Business & Money8 months ago
Business & Money8 months agoEquity Group Announces Kshs 15.1 Billion Dividend Amid Strong Performance
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoFred Okengo Matiang’i vs. President William Ruto: A 2027 Election Showdown
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoIchung’wah Faces Mt. Kenya Backlash Over Gachagua Impeachment Support
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoPresident Ruto’s Bold Cabinet Dismissal Sparks Hope for Change
-
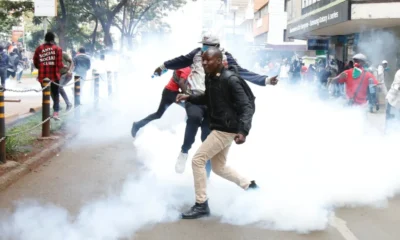
 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoKenya Grapples with Investor Confidence Crisis Amid Tax Protest Fallout
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoPresident Ruto’s Lavish Spending Amid Kenya’s Economic Struggles Sparks Outrage
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoJohn Mbadi Takes Over Kenya’s Treasury: Challenges Ahead
-

 Business & Money1 week ago
Business & Money1 week agoMeet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?





