Politics
UDA Fightback: The Fall of Cleophas Wakhungu Malala
Cleophas Wakhungu Malala’s dramatic fall within UDA underscores the volatile nature of Kenyan politics, marked by intense power struggles and shifting alliances. As UDA navigates internal divisions to secure its future, Malala faces the challenge of redefining his political strategy to stay relevant in this dynamic landscape.

By Charles Wachira
In a dramatic twist within Kenya’s United Democratic Alliance (UDA), the rapid rise and sudden fall of Cleophas Wakhungu Malala serves as a vivid example of the intense power struggles that characterise Kenyan politics. Malala, who had quickly ascended the ranks of the ruling party, now finds himself ousted from his influential role, a victim of internal party dynamics and rivalries.
The Rise of Cleophas Wakhungu Malala
Cleophas Malala first entered the national political spotlight in 2017 when he won the Kakamega County Senate seat under the Amani National Congress (ANC) banner. His victory was notable for its timing and context—coming at a time when the opposition was mounting a formidable challenge against the Jubilee administration. Malala’s fiery rhetoric and charismatic leadership made him a prominent figure within the opposition.
However, the shifting political landscape in 2022 saw Malala align himself with Deputy President William Ruto’s UDA party. This move was seen as opportunistic and strategic, as Malala sought to secure his political future in the rapidly changing environment. His decision to ditch the ANC for UDA was rewarded in February 2023, when he was appointed as the Secretary General of UDA, replacing Veronica Maina.
Malala’s appointment was widely interpreted as a move to solidify UDA’s influence in Western Kenya, where he was expected to deliver the Luhya vote. His role as Secretary General placed him at the heart of UDA’s operations, making him one of the most influential figures in the party.
The Power Struggles Within UDA
Malala’s tenure as Secretary General was marked by significant internal challenges. His assertive approach to party leadership and attempts to centralise decision-making created friction within UDA. Reports emerged of his clashes with key party figures, including those within President William Ruto’s inner circle. These tensions were compounded by his perceived closeness to Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua, which led to suspicions that Malala might be positioning himself for even higher office.
By mid-2024, these internal struggles had reached a boiling point. Malala openly accused UDA Chairperson Cecily Mbarire and Majority Leader Kimani Ichung’wah of orchestrating his ouster, ostensibly due to his support for the embattled Deputy President Gachagua. These accusations highlighted the deep divisions within the party and the extent to which internal power dynamics were influencing key decisions.
The Fall: A Calculated Move?
On August 15, 2024, Malala was officially removed from his position as UDA Secretary General, a move that took many by surprise. His replacement, Hassan Omar, the party’s Vice Chairperson, had been serving on an interim basis before his permanent appointment. The lack of fanfare surrounding Malala’s removal stood in stark contrast to the grand announcement of his appointment just a year earlier.
Political analysts believe that Malala’s fall was not merely the result of his performance but was driven by deeper fears among UDA’s leadership. His ambitions and growing influence were seen as a threat by those within the party who were determined to maintain control. A senior UDA official, who preferred to remain anonymous, commented on the situation:
“Malala’s removal was inevitable. In UDA, loyalty to the top leadership is paramount, and Malala’s growing closeness to Gachagua made him a liability. The party could not afford to have a potential rival gaining too much power.”
The Political Repercussions
Malala’s ouster has significant implications for both UDA and Kenya’s broader political landscape. For UDA, it represents a consolidation of power among a select group closely aligned with President Ruto. The removal sends a clear message to other ambitious politicians within the party: loyalty to the established leadership is non-negotiable.
For Malala, this represents a critical juncture in his political career. Whether he can recover from this setback remains uncertain, but the history of Kenyan politics suggests that he may yet find a path back to relevance. However, without a strong political base or clear platform, his options may be limited.
The Broader Context: A Party in Flux
The fall of Cleophas Malala underscores the challenges facing UDA as it navigates its internal tensions. While the party remains dominant, these divisions could threaten its cohesion, particularly as the 2027 general elections approach. Malala’s removal may also have repercussions in Western Kenya, where his influence was key to UDA’s strategy. His exit could provide an opportunity for the opposition, particularly the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM), to regain ground in the region.
Conclusion
The fall of Cleophas Wakhungu Malala is a potent reminder of the volatility of Kenyan politics. His rise and fall within UDA highlight the intense power struggles and shifting alliances that define the political landscape. As UDA looks to the future, it must address these internal divisions to maintain its hold on power, while Malala must reassess its political strategy to remain relevant in this ever-changing environment.
Keywords–Cleophas Malala UDA ouster: UDA power struggles Kenya: Malala rise and fall: William Ruto UDA leadership: Hassan Omar replaces Malala.
Politics
Martha Karua’s Memoir: A Journey of Leadership and Resilience

: Discover Martha Karua’s memoir, Against the Tide, as she reflects on her
political career, struggles, and triumphs in Kenya’s fight for justice and
leadership.
Martha Wangari Karua, born on September 22, 1957, in Kirinyaga District, launched her
memoir, Against The Tide, on Sunday, November 17, 2024.
This memoir, the culmination of nine years of writing, offers an insightful and personal
look into Karua’s remarkable journey as a lawyer, activist, and politician.
Known for her staunch advocacy for justice, tireless efforts against corruption, and bold
leadership, Karua has become one of Kenya’s most respected political figures.
“Writing this book has been a labour of love; the love I have for my country
and its people, the struggles I have endured, and the unwavering
commitment to building a better Kenya,” Karua shared at the launch,
reflecting on the challenges and triumphs that have defined her career.
A Curious Childhood and Early Inspirations
Growing up in Kimunye village, Karua’s inquisitiveness often led her to challenge the
status quo. Despite being a source of concern for her parents—both teachers—her
curiosity became the foundation of her intellectual pursuits.
“My close family had been supportive and patient, my dad and teachers
exhibited patience with me,” Karua recalls.
Her father, a prominent figure in her early life, sparked Karua’s interest in law,
particularly after she accompanied him to court as a child and became fascinated by the
respect magistrates commanded.
“When I was in primary school, I accompanied my dad to court on a traffic
matter. We had gone to Kerugoya, then we passed by the court. I liked the
attention the magistrate was getting, and upcountry they were being called
‘Judge,’” she explains.
Karua’s education at Nairobi Girls’ School fostered her independence, where she was
encouraged to express her opinions freely—a crucial factor in the development of her
leadership qualities.
Political Awakening
Karua’s political activism began within the Law Society of Kenya (LSK), where she and
other members challenged government excesses. This marked the beginning of her
deep commitment to national change.
“I realised that just as I had in the law society activism, it’s not enough to
complain about what is not being done.
It’s also important to get there and do what you think should be done. I was
seeking to be a part of the solution,” she explained.
Her decision to join active politics in 1992 led to her election as the Member of
Parliament (MP) for Gichugu, a position she held for four terms.
This transition marked her rise to national prominence, where she became renowned
for her principles, adherence to the rule of law and advocacy for women’s rights. Over
time, her steadfast nature earned her the nickname “The Iron Lady.”
From Law School to Legal Practice
Karua’s passion for law drove her to the University of Nairobi, where she earned her law
degree in 1980 and was admitted to the bar in 1982.
At just 24 years old, she began her career as a magistrate. However, financial
constraints led her to private practice in 1987, where she grew her firm, Martha Karua &
Co. Advocates, and advocated for human rights during Kenya’s politically turbulent
years under President Daniel arap Moi.
“When I entered the judiciary as a magistrate, I was earning Sh3,000. When
I got a family, the salary was not good enough,” Karua explains.
Her work in public service and private practice led to her being conferred Senior
Counsel 38 years later, following a career marked by significant legal accomplishments.
A Pivotal Role in the 2007 Election Crisis
In her memoir, Karua recounts the dramatic aftermath of the 2007 elections, when the
Electoral Commission of Kenya declared Mwai Kibaki the winner amid accusations of
fraud.
Despite widespread protests from the opposition, led by Raila Odinga, Karua took
immediate action to ensure Kibaki was sworn in.
The swearing-in ceremony, held on December 30, 2007, took place at State House,
Nairobi, despite the chaotic situation.
“The swearing-in had to be done immediately. Kibaki was declared the winner, and
according to the Inter-Parties Parliamentary Group (IPPG) amendment, the President
was to be sworn in as soon as he was declared,” Karua explained.
The action was necessary, she asserted, to maintain order during a tense political
period.
“How else could the swearing-in have been conducted? It was vital to swear
him in immediately,” she added.
Despite the political turmoil, Karua stands by her decision:
“I did what was right, and I stand by that decision. Even tomorrow, I will do
what is right. I have no regrets about the role I played as Kibaki’s agent and
the vote I cast for him,” she said.
However, the aftermath of the election saw post-election violence, which led to tribal
clashes, destruction, and loss of life. Karua expressed regret for the violence that
followed:
“We regret the loss of life, the destruction of property, and the displacement
of people. We also regret our failure as leaders, which could have led the
country into an abyss.”
Lessons from Leadership and Regrets
In her memoir, Karua reflects candidly on her political journey, including her decision to
run for president in 2012, which she now considers a misstep.
“The people of Gichugu elected me. I believe if I had gone for the
parliamentary seat instead of the presidency in 2012 or any local seat, I
would still be elected. I had bitten more than I could chew,” she admits.
Despite the loss, Karua stands firm in her principled approach to politics, particularly
during the constitutional review under President Mwai Kibaki’s administration.
“The issue of refusing to anchor the agreement in the Constitution was
pivotal. Kibaki wanted to accommodate Raila and his group in government
but still retain the ability to appoint and fire just like before. However, Raila and his group, having been fired in 2005, wanted it enshrined in the Constitution,” she explains.
A Legacy of Resilience
Karua’s story is not just one of triumph, but also resilience in the face of adversity,
including losses and betrayals. Reflecting on her journey, she writes:
“Thirty-eight years later, I was conferred to the rank of Senior Counsel
following an illustrious career in public service and private practice,
successfully arguing cases that have set legal precedence. It has not been
easy. I have faced each tide that has come my way and overcome.”
Against The Tide: A Testament of Courage
This memoir, which took nearly a decade to complete, stands as a testament to Karua’s
unwavering resolve to confront challenges head-on.
For anyone seeking inspiration from one of Kenya’s most iconic leaders, Against The
Tide offers a story of resilience, leadership, and the relentless pursuit of justice.
“Against The Tide is about overcoming adversity. It’s about resilience,”
Karua declared.
Politics
Somaliland Elects Opposition Leader Irro as New President
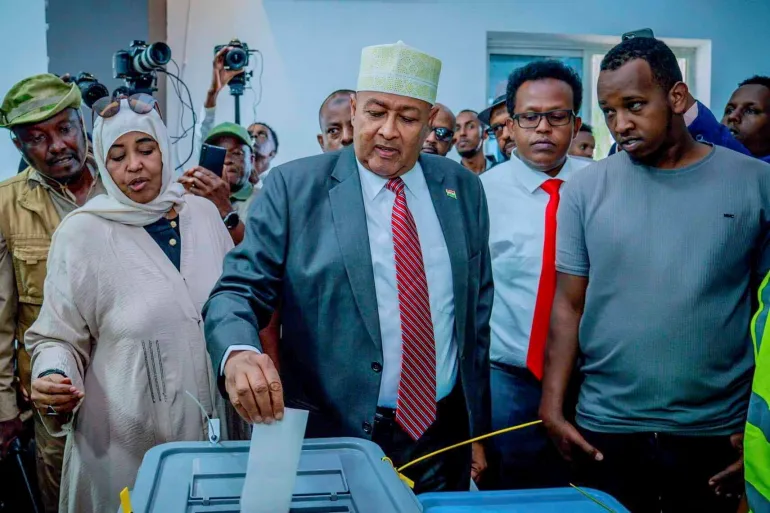

:Abdirahman Irro wins Somaliland’s 2024 presidential election with 64% votes,
signalling change. Over 1M registered voters participated peacefully
Somaliland’s presidential election, held on November 13, 2024, resulted in a decisive victory for Abdirahman Mohamed Abdullahi Irro of the Wadani Party.
Preliminary results indicated that Irro received approximately 64% of the votes, with Muse Bihi Abdi, the incumbent president from the Kulmiye Party, trailing at 35%.
The third candidate, Faysal Ali Warabe of the UCID Party, garnered less than 1% of the votes.
This election, initially scheduled for 2022, faced delays due to economic and political challenges but proceeded peacefully with over 1 million registered voters participating in over 2,000 polling stations.
Key Issues and Electoral Dynamics
The election was a referendum on governance, with voters expressing dissatisfaction with Muse Bihi Abdi’s administration, particularly regarding economic stagnation, rising unemployment, and issues of democratic space.
Irro’s Wadani Party campaigned on promises of economic reforms, improving international
recognition for Somaliland, and fostering greater inclusivity in governance.
Voter Turnout and Observations
Despite logistical challenges, approximately 680,000 voters cast their ballots. Observers from
ten nations praised the National Electoral Commission (NEC) for conducting a transparent
process.
No major security incidents were reported, showcasing Somaliland’s commitment to democratic principles.
Significance of the Win
Irro’s victory marks a significant shift in Somaliland’s political landscape.
As the leader of the opposition, his administration is expected to focus on addressing
longstanding economic and social grievances while seeking greater international legitimacy forSomaliland, which has remained diplomatically isolated since declaring independence in 1991.
The peaceful transfer of power further reinforces Somaliland’s reputation as a beacon of
democracy in the Horn of Africa The official results are expected to be announced by November 21, 2024, cementing Irro’s position as Somaliland’s new
Politics
Fred Matiang’i Hires Canadian Firm Dickens & Madson for 2027 Bid

: Fred Matiang’i partners with Dickens & Madson for $250K to boost his 2027
presidential campaign, focusing on lobbying and strategic global support.
Former Kenyan Interior Cabinet Secretary Fred Matiang’i has taken a bold step toward the 2027 presidential race by hiring Canadian lobbying firm Dickens & Madson. The firm, led by
controversial political consultant Ari Ben-Menashe, signed an agreement with Matiang’i on July 13, 2024. The deal reportedly involves a $250,000 (about KSh 32 million) fee, covering services designed to build international support for Matiang’i’s political ambitions over the coming years.
Scope of Services
Dickens & Madson is tasked with lobbying influential governments, including the U.S., U.K., and Japan, and international organisations to align them with Matiang’i’s bid. Their deliverables also include formulating strategies to enhance his political campaign and improve his global image.
This approach mirrors the firm’s previous engagements, where they used diplomatic channels to influence policies and secure favourable positions for their clients.
Previous Work
The firm is no stranger to high-profile and often controversial political campaigns. It has worked with Zimbabwean President Emmerson Mnangagwa to promote land deals and improve Zimbabwe’s international standing. Dickens & Madson’s client portfolio also includes various governments and individuals facing sanctions or international scrutiny, highlighting their reputation for navigating complex geopolitical terrains.
Implications for 2027
Matiang’i’s decision to engage a firm with such a record underscores his intention to leverage
international networks to counter President William Ruto’s administration.
While the move signals strategic ambition, it also invites scrutiny, given the firm’s controversial history and the polarised perception of Matiang’i’s leadership legacy This development sets the stage for a high-stakes election, as Matiang’i aims to position himself as a credible alternative to Ruto, drawing on both local and international support to bolster his campaign.
-

 Business & Money8 months ago
Business & Money8 months agoEquity Group Announces Kshs 15.1 Billion Dividend Amid Strong Performance
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoFred Okengo Matiang’i vs. President William Ruto: A 2027 Election Showdown
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoIchung’wah Faces Mt. Kenya Backlash Over Gachagua Impeachment Support
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoPresident Ruto’s Bold Cabinet Dismissal Sparks Hope for Change
-
 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoKenya Grapples with Investor Confidence Crisis Amid Tax Protest Fallout
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoPresident Ruto’s Lavish Spending Amid Kenya’s Economic Struggles Sparks Outrage
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoJohn Mbadi Takes Over Kenya’s Treasury: Challenges Ahead
-

 Business & Money1 week ago
Business & Money1 week agoMeet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?















