Politics
Ruto-ODM Alliance: Impact on Luo Nyanza and Kenya’s Future
William Ruto’s connection with Raila Odinga dates back to 2007 when they were both prominent figures in the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM). As a key supporter of Raila’s presidential campaign during the fiercely contested 2007 elections, Ruto played an influential role within ODM. Although Raila ultimately did not secure the presidency, this political alliance was pivotal for Ruto, enhancing his influence in Rift Valley politics.
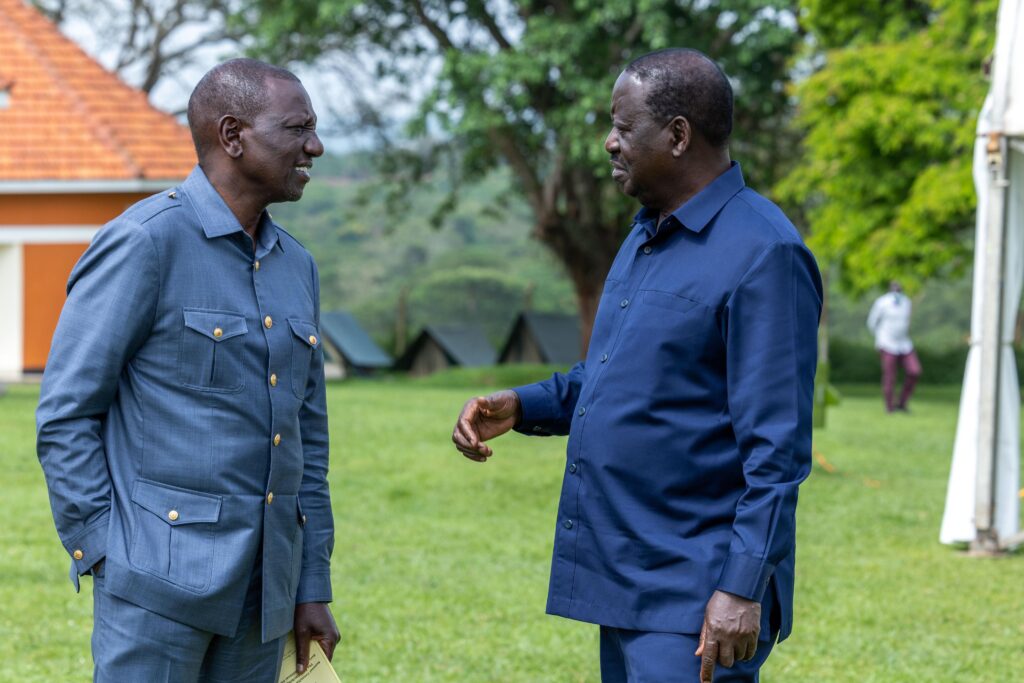

:Ruto’s Strategic ODM Alliance: What Luo-Kalenjin Unity and Gachagua’s Impeachment Could Mean for Kenya’s 2027 Elections
By Charles Wachira
In a move that sent shockwaves through Kenya’s political landscape, on July 24, 2024, President William Ruto nominated four senior-ranking members of the opposition ODM party into his new broad-based government. This decision, unprecedented in recent history, raised questions about its impact on the ODM political base in Luo Nyanza and the broader implications for Kenya’s political future, particularly considering Ruto’s pledge to nominate a female deputy president and the brewing tensions with Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua.
The history between Ruto and Raila Odinga, leader of the ODM party, is a long and complex one. The two men, who had once been political allies, found themselves on opposite sides during the 2022 general elections. Ruto, a formidable opponent of Raila, ran against him on a populist platform that promised economic transformation under the Kenya Kwanza Alliance. Raila, backed by the then-incumbent President Uhuru Kenyatta, represented the Azimio la Umoja coalition, advocating for continuity in governance and reforms aimed at social inclusion.
The Ruto-Raila Political History: From Allies to Rivals
William Ruto’s relationship with Raila Odinga goes back to 2007 when both were part of the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM). Ruto, a key player in ODM, supported Raila’s presidential bid in the highly contested 2007 elections. Although Raila did not win, the political partnership marked a high point for Ruto’s career, solidifying his influence in Rift Valley politics.
However, the alliance began to crack after the 2010 constitutional referendum, when Ruto broke away from Raila over disagreements regarding the new constitution’s provisions. The split widened, and by 2013, Ruto had formed an alliance with Uhuru Kenyatta, effectively leaving Raila’s political camp. This partnership with Kenyatta paved the way for Ruto to become Kenya’s deputy president. Raila, on the other hand, remained a key opposition figure, criticizing the government’s policies and vying for the presidency in the 2013 and 2017 elections.
The 2022 election further deepened the rivalry between the two. Raila was favored by Kenyatta, while Ruto, now running independently, positioned himself as the “hustlers’ candidate,” championing the cause of ordinary Kenyans. Ruto’s victory in the 2022 polls, despite Raila’s strong challenge, solidified his political base but also intensified the animosity between the two camps.
The ODM Move: What’s in it for Luo Nyanza?
The decision to incorporate ODM leaders into the Ruto administration represents a political gamble for both sides. For Ruto, the move appears to be a calculated attempt to co-opt opposition forces, thereby reducing the pressure from Raila’s ODM, which commands significant support in Luo Nyanza. By including opposition figures in his government, Ruto not only blurs the lines between the ruling party and opposition but also fractures the opposition’s ability to mount a cohesive challenge in future elections.
For ODM, agreeing to join the Kenya Kwanza administration is an equally strategic move, likely driven by pragmatism. Raila Odinga, despite losing the 2022 elections, continues to be a towering figure in Luo Nyanza politics. However, the opposition has found itself increasingly sidelined, with limited influence over national policy. By allowing some of his party members to be incorporated into Ruto’s government, Raila likely aims to maintain a foothold in national politics and secure resources and influence for his region.
Luo Nyanza has long been the bedrock of opposition politics, and ODM’s move risks alienating its core supporters. However, Raila may be betting that the benefits of being part of the government, in terms of regional development and political influence, outweigh the potential backlash from his traditional support base. The integration of ODM into the Kenya Kwanza government also weakens any potential opposition unity that could challenge Ruto in 2027.
Ruto’s Broader Strategy: Is Gachagua’s Future in Doubt?
The inclusion of ODM members into the government cannot be viewed in isolation. It comes at a time when President Ruto’s relationship with Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua has been under increasing strain. Gachagua, a key player in securing the Mt. Kenya vote for Ruto in 2022, has been a vocal and controversial figure, often clashing with other members of the Kenya Kwanza coalition and causing friction within the administration.
On March 7, 2024, Ruto made a significant pronouncement, pledging that his party would have a female deputy president in the near future. This declaration was widely interpreted as a signal that Gachagua’s days as deputy president may be numbered. The timing of this announcement, combined with the inclusion of ODM figures, has led to speculation that Ruto is quietly positioning himself for a future without Gachagua.
With the impeachment motion against Gachagua looming, led by MPs such as Mwengi Mutuse, Ruto’s recent moves could be seen as laying the groundwork for the deputy president’s removal. By building a broader coalition that includes ODM members, Ruto may be seeking to secure enough parliamentary support to push through Gachagua’s impeachment and install a new deputy—perhaps a female leader as he promised.
The Prospects of a Luo-Kalenjin Alliance
One of the most intriguing questions emerging from this political realignment is whether a Luo-Kalenjin alliance, facilitated by Ruto and Raila, could secure Ruto’s presidency in the 2027 elections. Historically, the two communities have been on opposite sides of Kenya’s political divide, but a rapprochement between Ruto and Raila could create a powerful electoral bloc.
Ruto’s Rift Valley base remains solid, and Raila’s influence in Luo Nyanza, despite the incorporation of ODM members into the government, is still formidable. A political alliance between the two could bring together these key voting blocs, creating a formidable force in Kenyan politics. However, such an alliance would come with significant risks. Ruto’s traditional supporters in Mt. Kenya, already uneasy about Gachagua’s sidelining, may view a partnership with Raila with suspicion, potentially fracturing the Kenya Kwanza coalition.
Broader Implications for Kenya’s Political Future
The alliance between Ruto and ODM members reflects the fluidity and pragmatism of Kenyan politics, where alliances shift quickly based on political necessity. For Ruto, the move offers a way to consolidate power, weaken the opposition, and prepare for future leadership battles, including the potential removal of Gachagua.
However, the broader implications of this alliance go beyond the immediate political calculations. By incorporating opposition members, Ruto is setting a precedent for a more inclusive, albeit politically complex, style of governance. This could reshape Kenya’s political landscape, moving away from the traditional adversarial relationship between government and opposition and toward a more collaborative, though fragile, arrangement.
Yet, the risks remain high. If the alliance fails to deliver tangible benefits for Luo Nyanza, Raila’s base could revolt, leaving ODM in a weakened position. For Ruto, the gamble lies in whether he can balance the competing interests of his coalition while preparing for the future—one that may include a new deputy president and a shifting alliance with the opposition.
As the political drama unfolds, one thing is clear: the next few years will be critical in determining the future of Kenya’s leadership. Whether through reconciliation or rupture, the Ruto-Gachagua alliance, coupled with the inclusion of ODM figures, will play a decisive role in shaping the country’s political trajectory leading up to the 2027 elections.
Keywords:Ruto-Gachagua alliance:ODM inclusion 2024:Luo-Kalenjin political alliance:Deputy president impeachment:Kenya 2027 elections
Politics
William Ruto’s First Year: Promises Made, Struggles Persist
President Ruto cannot fulfil his manifesto unless he curbs runaway corruption and holds culprits accountable. The rule of law requires recovering proceeds of crime and prosecuting offenders for economic sabotage. This strategy would reduce the need to overburden Kenyans with taxes and additional borrowing.
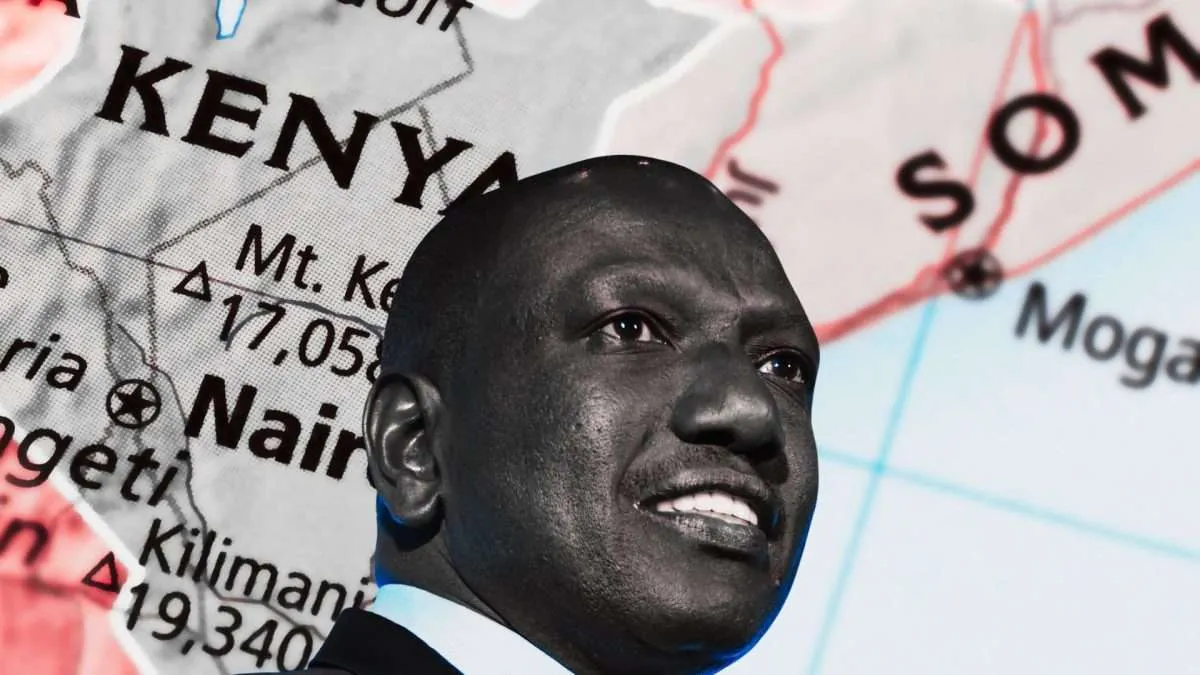

: Kenya’s President William Ruto faces challenges in fulfilling promises on governance, the economy, and national cohesion. Can he turn things around before 2027?
It’s more than a year since President William Ruto was sworn into office as Kenya’s fifth president.
He took office during a period of rising food and fuel prices, high unemployment, and a troubling debt burden in Kenya.
During the election campaign, Ruto promised to fix an economy afflicted by corruption and ineptitude. He promised to entrench good governance and place the poor at the centre of economic policy.
He pledged to address ethnicised politics and to uphold constitutionalism and the rule of law.
Ruto’s promises were significant. The rule of law and constitutionalism are key to economic planning and development, governance and equitable sharing of national resources.
They are the guardrails against impunity, democratic backsliding, lawlessness and political instability.
Throughout Kenya’s postcolonial period, the political elite have exploited ethnicity to obtain power at the expense of the collective well-being and social cohesion.
Elite entitlement has also weakened state institutions, leading to corruption and impunity.
I have studied democratic transitions, conflict and state building and elections in Africa.
My 2018 book examined how the political class had exploited ethnicity for political and economic advantage, resulting in weak and even dysfunctional state institutions in Kenya.
In his election campaign, Ruto identified the major issues that required urgent attention.
He addressed issues that needed swift action without constitutional changes, such as thawing the tension between the executive and the judiciary, decoupling the police finances from the executive, and taking port operations back to the coastal city of Mombasa from the inland town of Naivasha.
But resolving Kenya’s economic hardships has proved a hard nut to crack, as his 9 November 2023 State of the Nation address acknowledged. Just over a year since he was sworn in, Ruto is no nearer to turning the Kenyan ship around.
ECONOMIC TURBULENCE
As a candidate, Ruto portrayed himself as an outsider to Kenya’s power matrix who was best placed to improve the living conditions of the poor and excluded. But the economy has not improved under his watch. If anything, living conditions have worsened.
The cost of living is higher after a steep increase in the petrol price and the local currency’s loss of value. Ruto’s government has imposed new and increased taxes on Kenyans, ostensibly to reduce or remove the need for external borrowing.
The government was quick to remove fuel and food subsidies but has been slow to address government wastage.
The government’s key strategy was to subsidise fertiliser to boost harvests and achieve food security. It remains to be seen whether this will happen.
More deliberate measures are required to turn around agriculture as the mainstay of the economy.
On the question of centring the poor and marginalised in governance, Ruto focused on the financial sector. The government rolled out the “Hustler Fund” to make credit more affordable.
But the fund’s impact on overall living standards through job creation, for instance, is likely to be cancelled out by a punitive tax regime and a struggling economy.
RULE OF LAW
Ruto’s first public event as president was to approve the appointment of six judges left in limbo by his predecessor, Uhuru Kenyatta. He also made good on his promise to allocate more funding to the judiciary.
However, to entrench the rule of law and constitutionalism calls for more than this. Judicial officers must act with utmost integrity. To affirm equality before the law, errant senior state officers and the political elite must face the law and if found guilty sanctioned decisively.
The Kenyan judiciary is still bedevilled by corruption that impedes access to justice. Disturbingly, it is seen as more inclined to punish the poor while letting the rich and political elite act with impunity.
Ruto himself has obeyed court rulings that went against him, unlike under Kenyatta, when disregard for the law was the norm. Critics, however, including the Law Society of Kenya, have accused his administration of disobeying court orders like his predecessor.
Ruto spoke out against extrajudicial and summary executions and enforced disappearances perfected by the police over the years.
He sought to accord the police financial and operational autonomy. Thus he transferred accounting for the police budget to the police as he had promised.
Despite these changes, a culture of impunity and lack of transparency continues to undermine the Kenyan police. Extrajudicial executions continue. The police must be placed under civilian oversight as envisaged under the constitution.
The failure to set up a commission of inquiry into state capture under his predecessor, as promised during campaigns, dented Ruto’s commitment to the fight against corruption. A year later, a commission of inquiry has not been formed and the issue seems to have been abandoned altogether.
It is unlikely that Ruto will fulfil his manifesto unless he reins in runaway corruption and the culprits are held to account.
The rule of law demands that proceeds of crime be recovered and offenders charged for economic sabotage. This approach would obviate the need to burden Kenyans with taxes and more borrowing.
NATIONAL COHESION
Appointments to government positions have been undermined by the age-old problems of recycling appointees, patronage, nepotism and ethnicity. Just as worrying are senior government officials publicly advancing exclusionary ethnic politics with impunity. Ruto must rein them in.
It is also a setback that Ruto acceded to talks to assuage the opposition elite who had resorted to violent protests against his historic victory. These elitist self-serving talks could lead to constitutional amendments creating more political positions under a cynically flawed logic that this approach enhances national cohesion.
This is an about-turn on Ruto’s part.
Ultimately national cohesion is Ruto’s pressing challenge.
Kenya is divided on many fronts – economic, ethnic, regional and religious – a legacy of previous governments.
Ruto needs to look beyond ethno-regional appointments. For legitimacy and transformation, he needs to ideologically reconnect with and dignify the “hustler nation”, the disenfranchised constituency that propelled him into power. Bar this, he could face an intensely contested reelection bid like his predecessors.
Politics
Rigathi Gachagua’s Impeachment: A Political Conundrum for Ruto’s Administration
Former Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua’s impeachment has transformed Kenya’s political landscape, marking the first event of its kind under the 2010 Constitution.
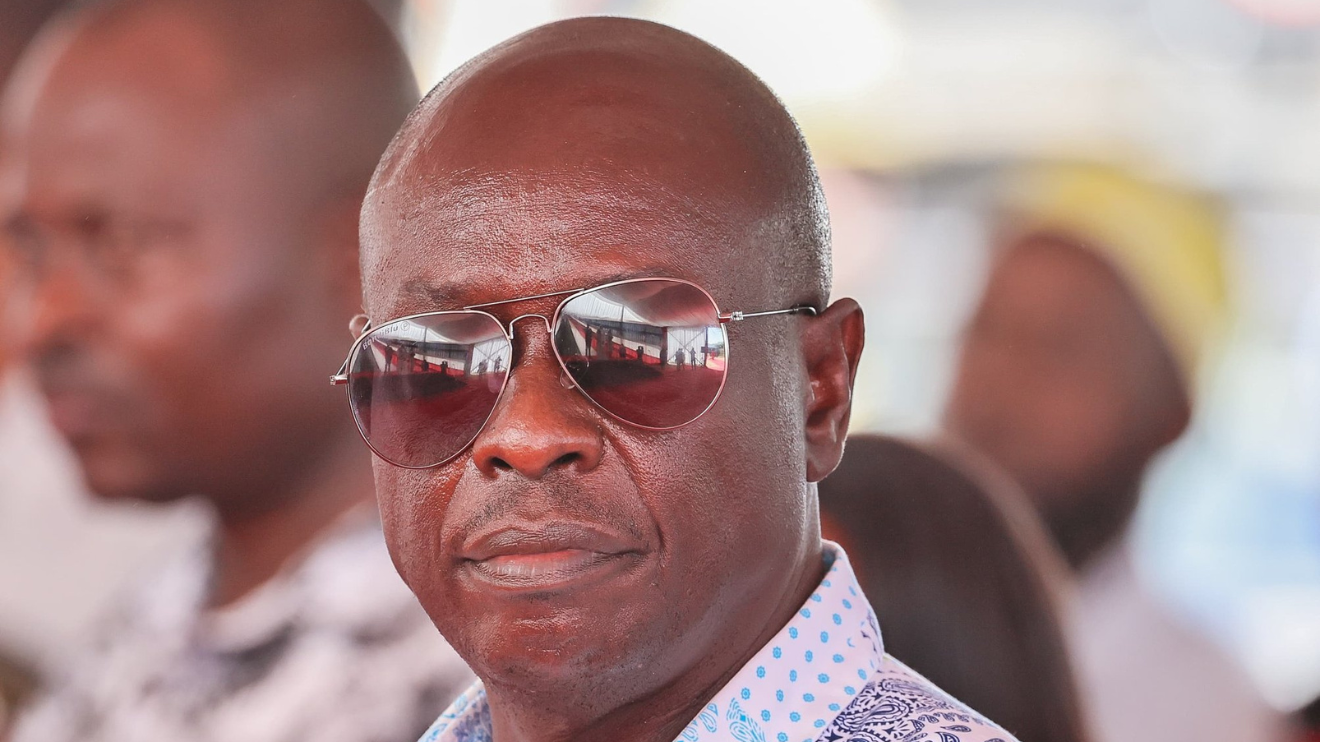

: Explore the political crisis after Rigathi Gachagua’s impeachment, its impact on William Ruto’s leadership, and the road to Kenya’s 2027 elections.
The impeachment of former Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua has upended Kenya’s political landscape, marking the first instance of such an event under the 2010 Constitution.
Accused of divisive politics and judicial interference, Gachagua’s ousting has ignited significant political tensions, particularly within the populous Mt. Kenya region, which has been a cornerstone of President William Ruto’s support base.
Gachagua has vocally criticised Ruto, describing his former ally as “vicious” and accusing him of orchestrating the impeachment.
In a fiery statement, Gachagua claimed, “The man I helped to become president has betrayed me,” while also alleging threats to his safety.
His impeachment has left the deputy presidency in limbo, with a court temporarily halting the appointment of Interior Minister Kithure Kindiki as his replacement.
Impact on Ruto’s Political Strategy
This political rift presents a dual challenge for Ruto. On one hand, it exposes cracks within the ruling coalition, with some legislators fearing backlash in their constituencies for supporting Gachagua’s removal.
On the other, it provides opposition leaders an opportunity to capitalise on perceived disunity within the government, potentially reshaping alliances as the 2027 elections approach.
Moreover, Gachagua’s removal has highlighted the volatile nature of Kenyan politics, where loyalty often shifts based on regional and ethnic dynamics.
Analysts believe Ruto must now tread carefully to maintain his hold over Mt. Kenya, a region critical to his electoral prospects.
The Way Forward
The administration must immediately stabilize governance by resolving the court dispute over Gachagua’s replacement or reconciling with dissenting factions.
Political analysts suggest that Ruto should focus on unifying his coalition and delivering tangible results to counter opposition narratives.
As Kenya moves closer to the 2027 polls, this episode underscores the importance of political cohesion and strategic messaging. Whether Ruto can overcome this challenge or face further fallout will significantly shape the country’s political trajectory.
Politics
Kenya Under Ruto: Transformative Leadership or Mounting Challenges?
Ruto’s policies have sparked mixed reactions on the social front. While he has taken a prominent role in addressing global challenges like climate change—evident in hosting a landmark summit that secured billions in clean energy investments—critics contend that his focus on international priorities has overshadowed pressing domestic concerns. Issues such as food insecurity and unemployment remain unresolved, leaving many Kenyans feeling neglected despite the administration’s ambitious global commitments.
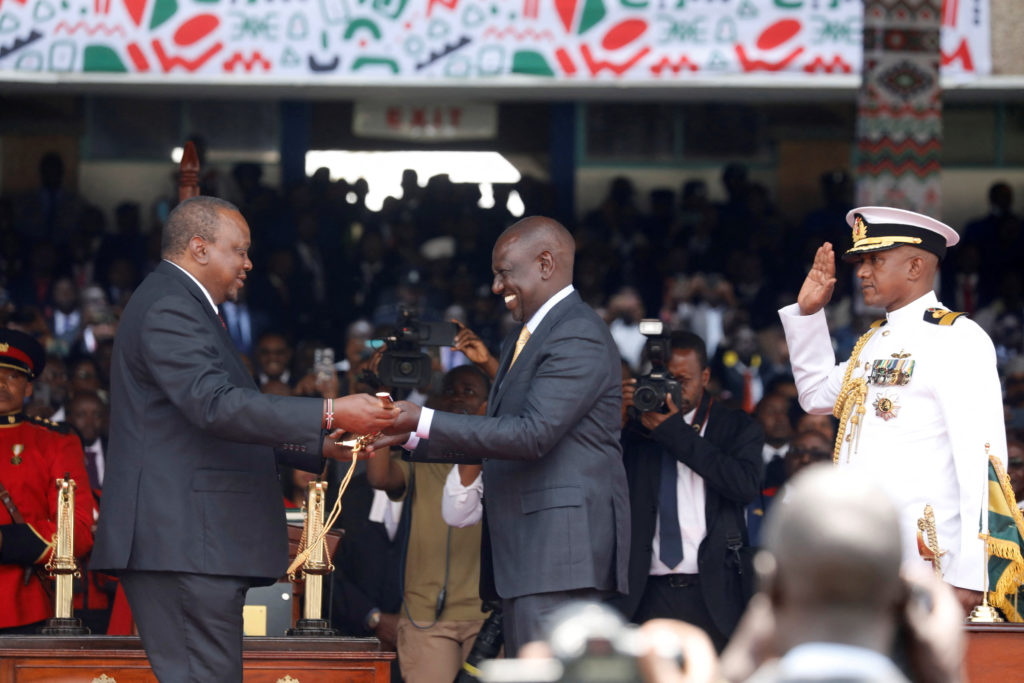

: Analyse President William Ruto’s leadership in Kenya, focusing on economic reforms, political strategies, and social challenges shaping the nation’s future.
Kenya’s President William Ruto, in office since September 2022, has faced mixed reviews regarding his leadership, particularly on economic, political, and social fronts.
Bold reforms, mounting challenges, and a mixed reception among citizens have marked his administration.
Economic Landscape
Ruto inherited an economy grappling with high debt levels ($69 billion), inflation, and global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the Ukraine war.
Despite efforts to stabilise the economy, including introducing new taxes and eliminating fuel subsidies to secure loans from the IMF and World Bank, these measures have strained ordinary Kenyans.
Household essentials, including sugar and beans, saw price hikes up to 61% and 30%, respectively. Inflation moderated to 6.7% in August 2023, but economic growth is projected to be slower than the 4.8% recorded in 2022
.Key initiatives such as the “Hustler Fund,” aimed at empowering small-scale entrepreneurs, have not delivered the expected outcomes, with some analysts like Ken Gichinga calling Ruto’s economic policies “ineffective.”
However, Ruto has also promoted local manufacturing and reduced reliance on imports to support job creation.
.
Political Strategy
On the political front, Ruto has shown determination to fight corruption.
His administration has introduced measures to track government spending and eliminate payroll fraud through a Unified Personal Identification system.
He has also emphasised accountability, stating, “We shall levy a surcharge against any officer who causes a loss of public resources.” However, critics question the effectiveness of these reforms, especially in light of continued economic hardships
Ruto’s administration faced opposition-led protests over rising living costs, which turned deadly, leaving 50 people dead.
These tensions underscore the political divisions and challenges in delivering tangible benefits to Kenyans
.Social Impact
Socially, Ruto’s policies have had polarising effects. While he champions global issues like climate change, hosting a major summit that attracted billions in clean energy investments, critics argue that his focus on international engagements has left domestic issues, such as food insecurity and unemployment, unresolved.
Analysts like Nerima Wako-Ojiwa emphasise that many Kenyans are now struggling with basic needs like food, highlighting a disconnect between the administration’s priorities and grassroots realities
.Broader Context and Future
Ruto has positioned himself as a reformer, focusing on transparency and economic restructuring.
However, his administration faces the twin challenge of delivering immediate relief to struggling Kenyans while maintaining long-term fiscal responsibility.
Supporters like Joseph Mwiti argue that transformative policies take time to bear fruit, reflecting cautious optimism about Ruto’s leadership.
In sum, President Ruto’s tenure has been characterised by ambitious reforms and significant headwinds. The success of his administration will depend on balancing economic recovery, political stability, and social equity in the coming years.
-

 Business & Money9 months ago
Business & Money9 months agoEquity Group Announces Kshs 15.1 Billion Dividend Amid Strong Performance
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoFred Okengo Matiang’i vs. President William Ruto: A 2027 Election Showdown
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoIchung’wah Faces Mt. Kenya Backlash Over Gachagua Impeachment Support
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoPresident Ruto’s Bold Cabinet Dismissal Sparks Hope for Change
-
 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoKenya Grapples with Investor Confidence Crisis Amid Tax Protest Fallout
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoPresident Ruto’s Lavish Spending Amid Kenya’s Economic Struggles Sparks Outrage
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoJohn Mbadi Takes Over Kenya’s Treasury: Challenges Ahead
-

 Business & Money2 months ago
Business & Money2 months agoMeet Kariuki Ngari: Standard Chartered Bank’s new CEO of Africa. What’s Next?





